Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
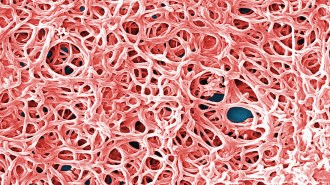
Health & MedicineHow to fight Lyme may lie in the biology of its disease-causing bacteria
The unusual molecular makeup of Borrelia burgdorferi, which causes Lyme disease, may hold clues for understanding and treating the tick-borne disease.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society$1.8 billion in NIH grant cuts hit minority health research the hardest
News of NIH funding cuts have trickled out in recent months. A new study tallies what’s been terminated.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTeens who want to quit vaping have another medication option
The drug varenicline, paired with counseling and text messaging support, helped teens and young adults abstain from vaping in a clinical trial.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDo cold-water plunges really speed post-workout muscle recovery?
A new study is among the first to look at whether cold or hot soaks help women’s muscles rebound from extreme exercise.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNeandertals invented bone-tipped spears all on their own
An 80,000-year-old bone point found in Eastern Europe challenges the idea that migrating Homo sapiens gave the technology to Neandertals.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyBritish tin might have fueled the rise of some Bronze Age civilizations
Chemical evidence of tin from coastal British sites reaching Bronze Age Mediterranean societies highlights a supply chain dispute.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
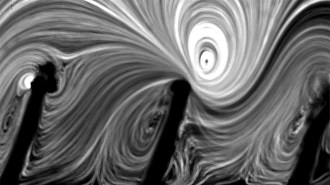
Health & MedicineLining medical stents with hairlike fuzz could fend off infections
Implanted tubes that transport bodily fluids can get gross. A lab prototype suggests a new vibration-based way to keep them clean and prevent infection.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA man let snakes bite him 202 times. His blood helped create a new antivenom
A new antivenom relies on antibodies from the blood of Tim Friede, who immunized himself against snakebites by injecting increasing doses of venom into his body.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Psychology
PsychologyPlaying this Minecraft game hints at how we learn in real life
A tailor-made version of Minecraft let researchers look at the success of learning individually or taking cues from others while foraging for fruit.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyChess players rely on familiar moves even when the game changes
In chess as in life, people use memory as a shortcut for decision-making. That strategy can backfire when the present doesn’t resemblance the past.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOzempic and Wegovy ingredient may reverse signs of liver disease
The diabetes and weight loss drug semaglutide reversed liver scarring and inflammation. It’s among several drugs in the works for the condition MASH.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyA Pueblo tribe recruited scientists to reclaim its ancient American history
DNA supports modern Picuris Pueblo accounts of ancestry going back more than 1,000 years to Chaco Canyon society.
By Bruce Bower