Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHeartburn drugs may raise stroke risk
Drugs used by millions for heartburn linked to increased risk of stroke.
By Laura Beil -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDespite Alzheimer’s plaques, some seniors remain mentally sharp
Plaques and tangles riddle the brains of some very old and very healthy people.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceProtein linked to Parkinson’s travels from gut to brain
Parkinson’s protein can travel from gut to brain, mouse study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDownside of yo-yo dieting is rise in heart disease risk
Yo-yo dieting hurts the heart, even if you’re not overweight.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChinese patient is first to be treated with CRISPR-edited cells
Researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 to engineer immune cells that were then injected into a patient with lung cancer, the journal Nature reports.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSounds and glowing screens impair mouse brains
Too much light and noise screws up developing mice’s brains.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRestless sleep associated with heart rhythm problems
Poor sleep, even without apnea, is tied to heart rhythm problems.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMarijuana use weakens heart muscle
Marijuana linked to dangerous heart stress.
By Laura Beil -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceZap to the head leads to fat loss
Stimulating the vestibular nerve led people to shed fat in a small trial.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCDC sounds alarm on STDs
The combined reported cases of three common sexually transmitted diseases reached a historic peak in 2015, a new CDC report says.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePopular painkiller doesn’t have more heart risks than others, study claims
A long anticipated trial of the drug Celebrex finds it poses no more risk to the heart than do similar painkillers, but critics cite flaws in the study.
By Laura Beil -
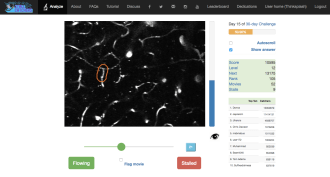 Life
LifeWebsite turns Alzheimer’s research into a game
A new game assists Alzheimer’s researchers in the hunt for stalled blood vessels in the brains of mice.