Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInstead of starving a cancer, researchers go after its defenses
There may be ways to block tumors from adapting and outrunning the body’s defenses.
By Laura Beil -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyPower may have passed via women in ancient Chaco Canyon society
DNA points to a 330-year-long reign of a maternal dynasty centered in New Mexico’s Chaco Canyon.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyLow-status chimps revealed as trendsetters
Outranked chimpanzees trigger spread of useful new behaviors among their comrades.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCommon fungus may raise asthma risk
The presence of a fungus in the infant gut can signal development of asthma by age 5.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFor Ebola patients, a few signs mean treatment’s needed — stat
A few criteria may help identify Ebola patients who need the most care.
-
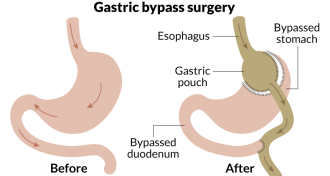 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGastric bypass controls diabetes long term better than other methods
Bariatric surgery outperforms other weight-loss measures in the longest-term study yet of diabetes outcomes.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBirth may not be a major microbe delivery event for babies
A study of mother-baby duos suggests that birth itself may not be the main event for getting microbes in and on babies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSee how long Zika lasts in semen and other bodily fluids
For most men infected with Zika, traces of the virus disappear from semen 81 days after symptoms begin. In other bodily fluids, Zika RNA is typically cleared even faster.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Psychology
PsychologyPhysically abused kids learn to fail at social rules for success
What physically abused kids learn about rewards at home can lead to misbehavior elsewhere.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRicin poisoning may one day be treatable with new antidote
Mice treated with a blend of antibodies survived even when treated days after exposure to ricin.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCold plasma puts the chill on norovirus
A new device uses cold plasma to kill foodborne pathogens.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineReaders respond to antibiotics, carbon bonds and more
Allergic overreactions, the possibility of silicon-based life and more in reader feedback.