Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. moms say their mental health is getting worse
A national survey finds that mothers of children ages 0 to 17 years report mental health declines from 2016 to 2023.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryLotions and perfumes affect the air near our skin
The personal care products suppress reactions between skin oils and ozone. It's not clear how, or if, this chemistry change might impact human health.
By Skyler Ware -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMales of this ancient human cousin weren’t always bigger than females
Molecular evidence from a 2-million-year-old southern African hominid species indicates sex and genetic differences in P. robustus.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyStudents’ mental health imperiled by $1 billion cuts to school funding
The Trump administration is cutting $1 billion in grants that support student mental health. That has educators worried.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePersonalized gene editing saved a baby, but the tech’s future is uncertain
The personalized CRISPR treatment could be the future of gene therapy, but hurdles remain before everyone has access.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHumans used whale bones to make tools 20,000 years ago
Ancient scavengers of the beached beasts turned their bones into implements that spread across a large area, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWet fingers always wrinkle in the same way
Pruney fingertips aren't swollen sponges — the wrinkles actually come from blood vessels constricting and pulling skin inward.
-
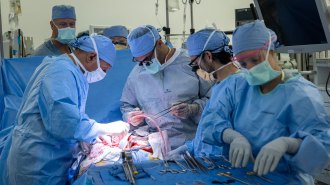 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIt’s tricky to transplant a bladder. How surgeons finally did it
The person who received the bladder is doing well, and the successful transplant could offer hope to thousands of people with bladder dysfunction.
By Payal Dhar -
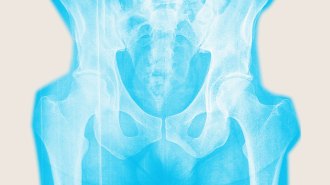 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDon’t wait until menopause to strengthen your bones
Screening for osteoporosis is recommended at age 65, but experts say women should be proactive about bone health long before that.
-
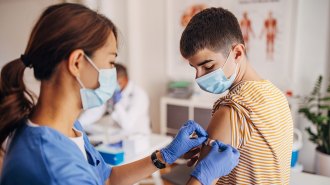 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFDA significantly limits access to COVID-19 vaccines
The new framework unveiled May 20 says new COVID-19 shots should go only to those ages 65 and up or with underlying medical conditions.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBiden’s prostate cancer is incurable, but it is treatable
Experts explain the science behind Biden's advanced prostate cancer diagnosis, including how common it is and what treatments are available.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsA ‘talking’ ape’s death signals the end of an era
Kanzi showed apes have the capacity for language, but in recent years scientists have questioned the ethics of ape experiments.
By Erin Wayman