Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen it comes to baby’s growth, early pregnancy weight may matter more than later gains
Women’s weight before and during the first half of pregnancy may be most important indicators of baby’s birth weight.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGlobal Virome Project is hunting for more than 1 million unknown viruses
Scientists are searching for viruses lurking in animals that could threaten human health.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyCave art suggests Neandertals were ancient humans’ mental equals
Ancient humans’ close relatives also created rock art and shell ornaments, studies assert.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, early organ transplants brought triumph and tragedy
In 1968, the liver transplant field had its first small successes. Now, more than 30,000 patients in the U.S. receive a donated liver each year.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new study eases fears of a link between autism and prenatal ultrasounds
On almost every measure, prenatal ultrasounds doesn’t appear to be related to a risk of developing autism, a recent study finds.
-
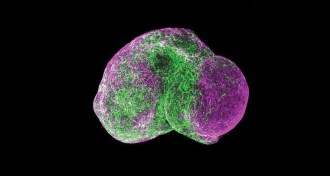 Humans
HumansHow to build a human brain
Organoids, made from human stem cells, are growing into brains and other miniorgans to help researchers study development
By Ingfei Chen -
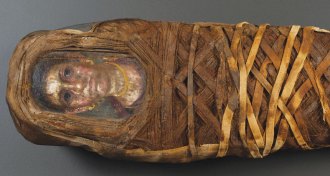 Archaeology
ArchaeologyModern tech unravels mysteries of Egyptian mummy portraits
A museum exhibit showcases what modern analytical tools can reveal about ancient Egyptian funerary portraits and mummies.
-
 Tech
TechThis stick-on patch could keep tabs on stroke patients at home
New wearable electronics that monitor swallowing and speech could aid rehabilitation therapy for stroke patients.
-
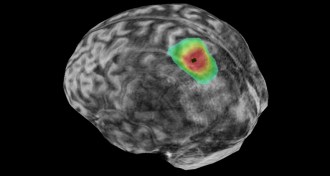 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTo hear the beat, your brain may think about moving to it
To keep time to a song, the brain relies on a region used to plan movement — even when you’re not tapping along.
By Dan Garisto -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyIn Borneo, hunting emerges as a key threat to endangered orangutans
Only small numbers of Bornean orangutans will survive coming decades, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsStudy debunks fishy tale of how rabbits were first tamed
A popular tale about rabbit domestication turns out to be fiction.
-
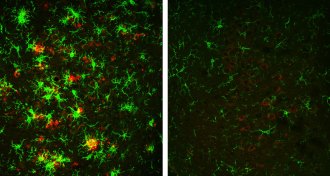 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCutting off a brain enzyme reversed Alzheimer’s plaques in mice
Inhibiting an enzyme involved in the production of Alzheimer’s protein globs also made old globs, or plaques, disappear in mouse brains.