Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyIn China, coffee shop habits show cultural differences tied to farming
Farming histories have shaped behavior in northern and southern China.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyClues to an Iron Age massacre lie in what the assailants left behind
Ancient Scandinavian massacre may reflect power struggles after Rome’s fall.
By Bruce Bower -
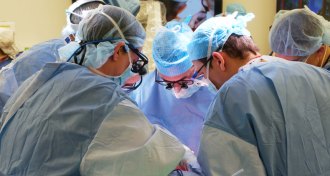 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe first penis-scrotum transplant is the latest to go beyond lifesaving
Advances that give patients new faces, hands and more aim to improve quality of life
-
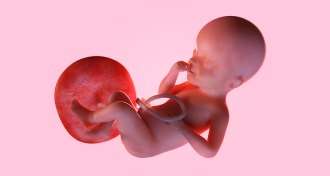 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThough often forgotten, the placenta has a huge role in baby’s health
Recent research in mice suggests that a lot of early problems in the embryo may actually have roots in the placenta.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyInformed wisdom trumps rigid rules when it comes to medical evidence
Narrative reviews of medical evidence offer benefits that the supposedly superior systematic approach can’t.
-
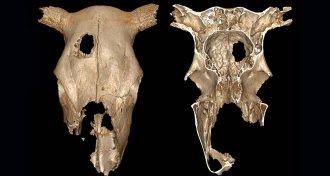 Anthropology
AnthropologyA hole in an ancient cow’s skull could have been surgery practice
Before performing skull operations on people, ancient surgeons may have rehearsed on cows.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThis ancient Maya city may have helped the Snake King dynasty spread
A rural hub in an ancient Maya state gets its due with some laser help.
By Bruce Bower -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA new plastic film glows to flag food contaminated with dangerous microbes
Plastic patches that glow when they touch some types of bacteria could be built into food packaging to reduce the spread of foodborne illness.
-
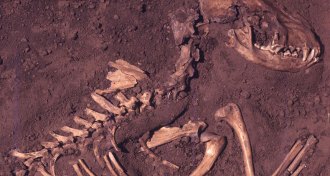 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDogs lived and died with humans 10,000 years ago in the Americas
Dogs unearthed at sites in Illinois were older than originally thought.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyTales of rampant suicide among Custer’s soldiers may be overblown
Few of Custer’s men killed themselves in the face of overwhelming Native American numbers at the Battle of the Little Bighorn, skeletal data suggest.
By Bruce Bower -
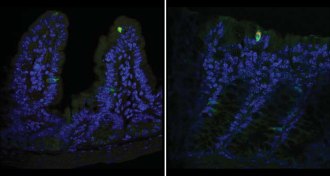 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis is how norovirus invades the body
Norovirus targets a rare type of gut cell, a study in mice finds.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSweet potatoes might have arrived in Polynesia long before humans
Genetic analysis suggests that sweet potatoes were present in Polynesia over 100,000 years ago, and didn’t need help crossing the Pacific.
By Dan Garisto