Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA mysterious dementia that mimics Alzheimer’s gets named LATE
An underappreciated form of dementia that causes memory trouble in older people gets a name: LATE.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow holes in herd immunity led to a 25-year high in U.S. measles cases
U.S. measles cases have surged to 704. Outbreaks reveal pockets of vulnerability where too many unvaccinated people are helping the virus spread.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy war’s emotional wounds run deeper for some kids and not others
Researchers examine why war’s emotional wounds run deep in some youngsters, not others.
By Bruce Bower -
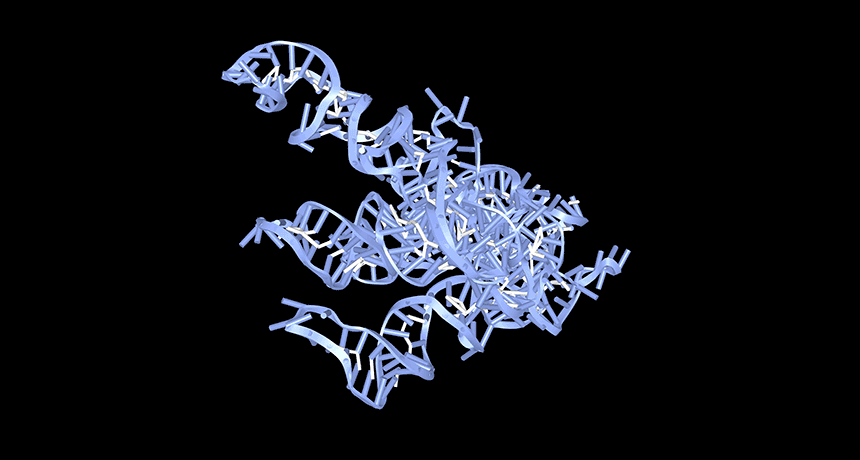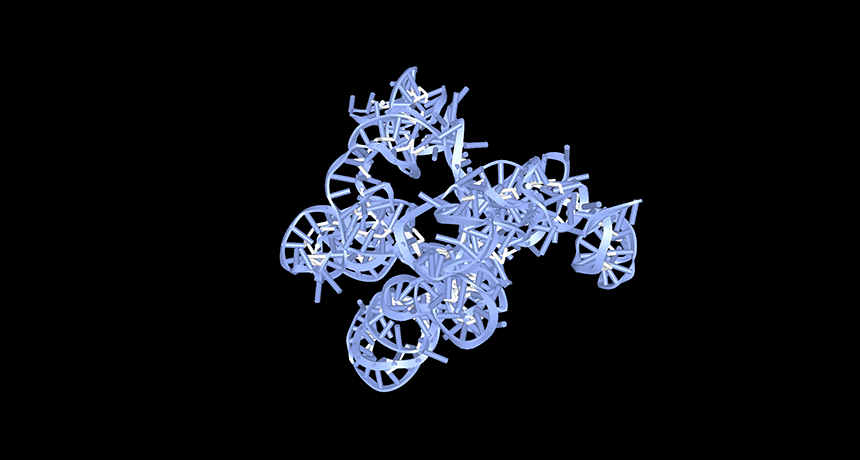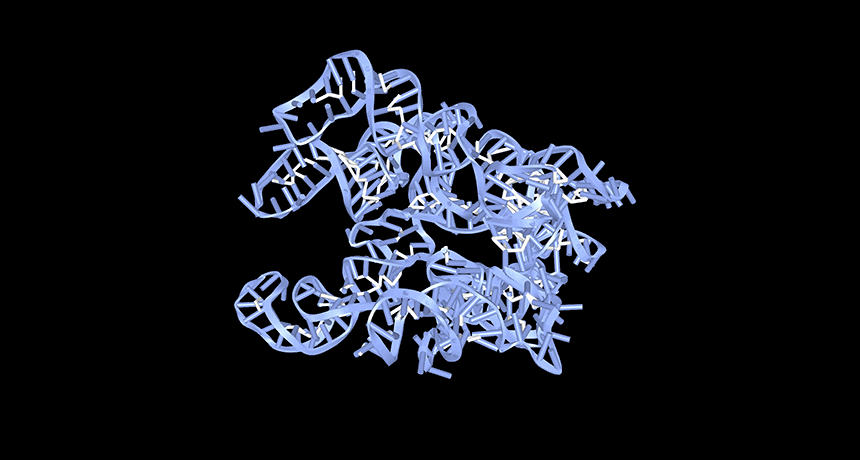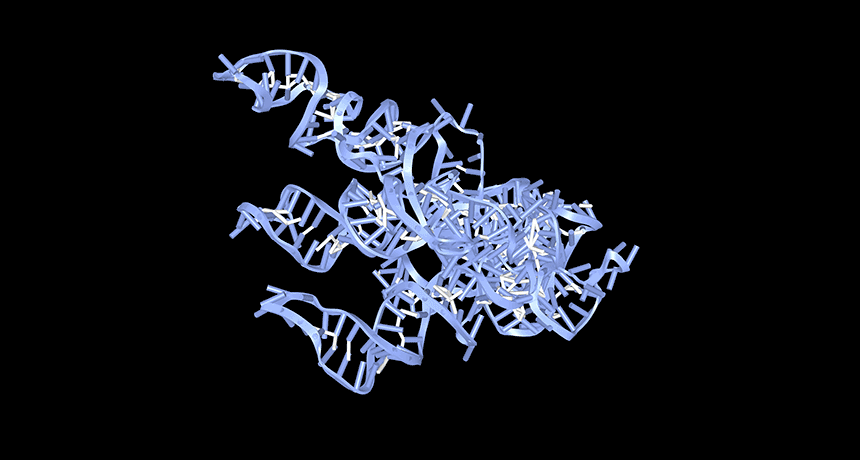 Genetics
GeneticsA lack of circular RNAs may trigger lupus
Researchers close in on how low levels of a kind of RNA may trigger lupus — offering hope for future treatments for the autoimmune disease.
-
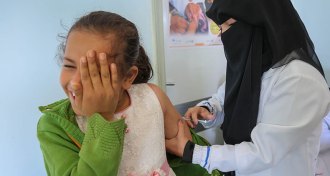 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. measles cases hit a record high since the disease was eliminated in 2000
Each year from 2010 to 2017, 21 million children did not get vaccinated against measles, according to UNICEF.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyExcavations show hunter-gatherers lived in the Amazon more than 10,000 years ago
Early foragers may have laid the foundation for farming’s ascent in South America’s tropical forests.
By Bruce Bower -
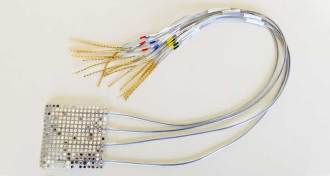 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA neural implant can translate brain activity into sentences
With electrodes in the brain, scientists translated neural signals into speech, which could someday help the speechless speak.
-
 Humans
HumansMedicaid expansion may help shrink health gaps between black and white babies
States that expanded Medicaid as part of the Affordable Care Act shrunk racial disparities between black and white infants, a new study shows.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Astronomy
AstronomySeeing very far away and hitting closer to home
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses the first-ever image of a black hole and what can be done to help young children with anxiety.
By Nancy Shute -
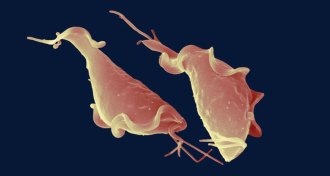 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow an obscure sexually transmitted parasite tangos with the immune system
Scientists are working out how Trichomonas vaginalis, one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections, causes problems in women and men.
By Amber Dance -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient sculptors made magnetic figures from rocks struck by lightning
Carved ‘potbelly’ stone sculptures suggest people in what’s now Guatemala knew about magnetism more than 2,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
PsychologyWhen anxiety happens as early as preschool, treatments can help
Researchers are seeking ways to break the link between preschool worries and adult anxiety.
By Sujata Gupta