Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSeth Shipman recorded a movie in DNA — and that’s just the beginning
Seth Shipman is developing tools that may reveal hidden biological processes.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMaryam Shanechi designs machines to read minds
Maryam Shanechi creates computer programs that link brain and machine to one day help patients with paralysis or psychiatric disorders.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsStanley Qi gives CRISPR a makeover to redefine genetic engineering
By adapting CRISPR/Cas9, Stanley Qi has given genetic engineers a plethora of new tools.
-
 Health & Medicine
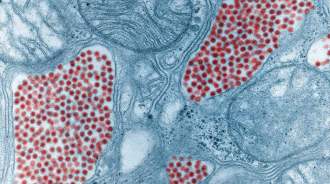
Health & MedicineRare eastern equine encephalitis has killed 9 people in the U.S. in 2019
2019 is the worst eastern equine encephalitis outbreak since tracking began in 2003, with 31 cases and nine deaths from the brain infection so far.
By Sofie Bates -
 Humans
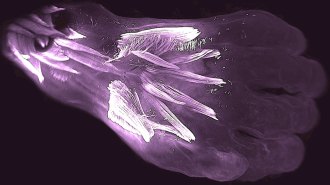
HumansHuman embryos have extra hand muscles found in lizards but not most adults
In developing human embryos, muscles are made, then lost, in a pattern that mirrors the appearance of the structures during evolution.
-
 Humans
HumansPersonalized diets may be the future of nutrition. But the science isn’t all there yet
How a person responds to food depends on more than the food itself. But what exactly is still a confusing mix of genes, microbes and other factors.
-
 Humans
HumansVaping-related illness reports have surged to 805 from 46 U.S. states
Twelve people have now died from lung injuries tied to e-cigarettes, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA mouse’s metabolism may follow circadian rhythms set by gut bacteria
While animals’ circadian clocks control functions from sleep to hormone release, gut bacteria dictate when mice’s small intestines take up fat.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists warned of marijuana’s effects on the unborn
In 1969, scientists warned about prenatal marijuana exposure. Researchers today are still untangling drug’s effect on fetuses.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRockland’s measles outbreak is over, but U.S. elimination status is still at risk
Officials in Rockland County in New York announced that their measles outbreak, which began October 1 of last year, is finally finished.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyBaby bottles may go back millennia in Europe
Europe’s early farmers used spouted vessels to wean infants, an analysis of residue from animal milk left in the containers suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
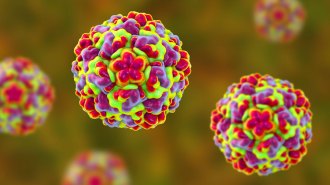
Health & MedicineDisabling one protein might one day lead to a cure for the common cold
Scientists have identified a protein in humans that some viruses, including those that cause colds, need to spread.
By Sofie Bates