Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
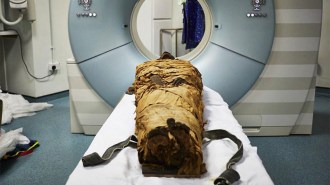
ArchaeologyA 3-D printed vocal tract lets an ancient mummy speak from beyond the grave
A re-created version of a mummy’s vocal tract reveals what this ancient Egyptian might have sounded like.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyMount Vesuvius may have suffocated, not vaporized, some victims
A new study suggests people living near Pompeii who hid in stone boathouses died a slower death when the volcano erupted in A.D. 79.
-
 Humans
HumansStress turns hair gray by triggering the body’s fight-or-flight response
A study in mice finds stress responses deplete cells that give hair its pigment, making the strand white.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient kids’ DNA reveals new insights into how Africa was populated
Four long-dead youngsters from west-central Africa have opened a window on humankind’s far-flung African origins.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe first U.S. case of a new coronavirus has been confirmed
After confirmation that a new coronavirus is transmissible between humans, U.S. health officials report a first case in Seattle.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHairy cells in the nose called brush cells may be involved in causing allergies
Some hairy cells in the nose may trigger sneezing and allergies to dust mites, mold and other substances, new work with mice suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
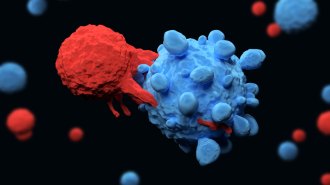
Health & MedicineExploding cancer cells can cause serious side effects in CAR-T cell therapies
Blocking a protein caused cancer cells targeted with CAR-T cell immunotherapy to shrink rather than burst, which may help reduce inflammation.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new drug lowers levels of a protein related to ‘bad’ cholesterol
The next clinical trial will determine if a drug targeting a protein that carries fat and cholesterol reduces the risk of heart attack and stroke.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyNeandertals dove and harvested clamshells for tools near Italy’s shores
The discovery of sharpened shells broadens the reputation of Stone Age human relatives: Neandertals weren’t just one-trick mammoth hunters.
By Bruce Bower -
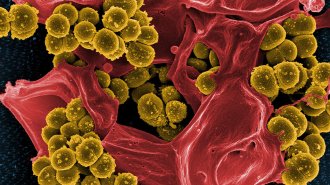 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobes slowed by one drug can rapidly develop resistance to another
Hunkering down in a dormant, tolerant state may make it easier for infectious bacteria to develop resistance to antibiotics.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAfter the Notre Dame fire, scientists get a glimpse of the cathedral’s origins
Researchers will tackle the scientific questions behind rebuilding Notre Dame, and learn more about its history.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat we know — and don’t know — about a new virus causing pneumonia in China
A newfound coronavirus is behind a mysterious outbreak of pneumonia in central China. Experts urge vigilance but say there’s no cause for panic.