Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCoronavirus’ spread in the U.S. may be a question of when, not if
The virus that causes COVID-19 is likely to gain a foothold in U.S. communities, says the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWe may be on the brink of a coronavirus pandemic. Here’s what that means
The coronavirus behind COVID-19 has not yet reached pandemic status, according the WHO, but we could be close.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologySouth Asian toolmaking withstood the biggest volcanic blast in 2 million years
Toolmakers continued to strike sharp-edged flakes as usual after a volcano’s colossal eruption around 74,000 years ago on what’s now Sumatra Island.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo tackle the new coronavirus, scientists are accelerating the vaccine process
Scientists are turning to nontraditional approaches to create vaccines and therapeutics that target the novel coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. drug deaths dipped in 2018, but cocaine and meth overdoses rose
In 2018, the rates of drug overdose deaths for methamphetamine and cocaine surpassed that of prescription opioids.
-
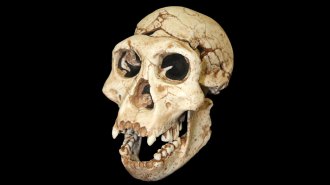 Humans
HumansThe earliest known hominid interbreeding occurred 700,000 years ago
The migration of Neandertal-Denisovan ancestors to Eurasia some 700,000 years ago heralded hookups with a resident hominid population.
By Bruce Bower -
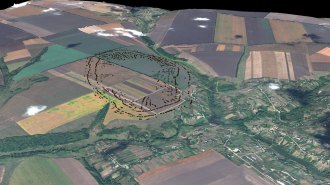 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient ‘megasites’ may reshape the history of the first cities
At least two ancient paths to urban development existed, some archaeologists argue.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNew cave fossils have revived the debate over Neandertal burials
Part of a Neandertal’s skeleton was found in a hole dug in the same cave in Iraqi Kurdistan where the “flower burial” was found in 1960.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVery few infants seem to be getting sick with the new coronavirus
Scientists tracking how the outbreak of a novel coronavirus is affecting young children and newborns haven’t seen many cases.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCoronavirus’s genetic fingerprints are used to rapidly map its spread
Fast and widespread scientific data sharing and genetic testing have created a picture of how the new coronavirus spreads.
-
 Humans
HumansSome West Africans may have genes from an ancient ‘ghost’ hominid
A humanlike population undiscovered in fossils may have passed helpful DNA on to human ancestors in West Africa starting as early as 124,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyFood residues offer a taste of pottery’s diverse origins in East Asia
Clay pots emerged in different places and for different reasons, starting at least 16,000 years ago, a study suggests.
By Bruce Bower