Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Humans
HumansUnderwater caves once hosted the Americas’ oldest known ochre mines
Now-submerged chambers in Mexico’s Yucatán Peninsula contain ancient evidence of extensive red ochre removal as early as 12,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine4 reasons not to worry about that ‘new’ swine flu in the news
Researchers identified a pig influenza virus that shares features with one that sparked the 2009 pandemic — that doesn’t mean another one is imminent.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy COVID-19 is both startlingly unique and painfully familiar
As doctors and patients learn more about the wide range of COVID-19 symptoms, the coronavirus is proving both novel and recognizable.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we’ve learned in six months of COVID-19 — and what we still don’t know
Six months into the new coronavirus pandemic, researchers have raced to uncover crucial information about SARS-CoV-2. But much is still unknown.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyMonkeys may share a key grammar-related skill with humans
A contested study suggests the ability to embed sequences within other sequences, a skill called recursion and crucial to grammar, has ancient roots.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy scientists say wearing masks shouldn’t be controversial
New data suggest that cloth masks work to reduce coronavirus cases, though less well than medical masks.
-
 Health & Medicine
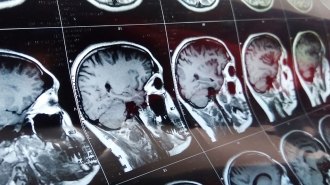
Health & MedicineStrokes and mental state changes hint at how COVID-19 harms the brain
In a group of people severely ill from the coronavirus, strokes, psychosis, depression and other brain-related changes come as complications.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe second-worst Ebola outbreak ever is officially over
As Congo grapples with COVID-19 and other disease outbreaks, the country’s 10th battle against Ebola has ended.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMillions of COVID-19 cases in the U.S. may have gone undiagnosed in March
Millions of people in the United States went to the doctor in March with influenza-like symptoms. Many may have had COVID-19, a study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
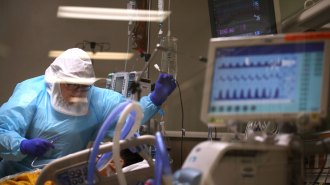
Health & MedicinePreventing dangerous blood clots from COVID-19 is proving tricky
Clinical trials of blood-clotting drugs have begun in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, as excessive clotting remains a complication of the disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 case clusters offer lessons and warnings for reopening
As restaurants, offices and other businesses open, trends in where and how COVID-19 transmission is happening could help guide re-entry strategies.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA from a 5,200-year-old Irish tomb hints at ancient royal incest
Ruling families in Ireland may have organized a big tomb project, and inbred, more than 5,000 years ago, a new study suggests.
By Bruce Bower