Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘The Origins of You’ explores how kids develop into their adult selves
A new book describes the interplay of nature and nurture as children, at least in Western societies, grow up.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
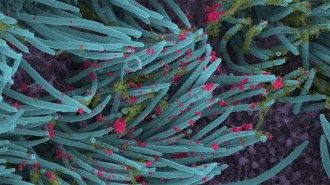
Health & MedicineLung cell images show how intense a coronavirus infection can be
Microscopic views reveal virus particles coating the hairlike cilia of an airway cell from the lungs.
-
 Health & Medicine
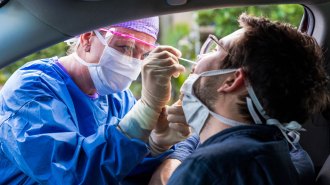
Health & MedicineTreatments that target the coronavirus in the nose might help prevent COVID-19
Scientists are developing and testing ways to prevent the virus from settling in prime nasal real estate.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCollege athletes show signs of possible heart injury after COVID-19
Four of 26 college athletes, who had mild or asymptomatic COVID-19, may have had myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle.
-
 Humans
HumansDrones find signs of a Native American ‘Great Settlement’ beneath a Kansas pasture
An earthwork buried under a cattle ranch may be part of one of the largest Native American settlements ever established north of Mexico.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
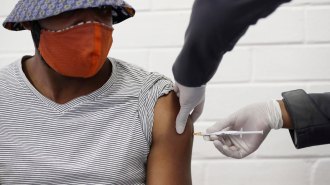
Health & MedicineHere’s what pausing the AstraZeneca-Oxford coronavirus vaccine trial really means
A coronavirus vaccine trial was paused after a volunteer had a possible adverse reaction. Such routine measures help ensure new vaccines are safe.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA sobering breakdown of severe COVID-19 cases shows young adults can’t dismiss it
Of about 3,200 people ages 18 to 34 hospitalized with COVID-19, nearly a quarter entered intensive care, and 10 percent were placed on ventilators.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyA stray molar is the oldest known fossil from an ancient gibbon
A newly described tooth puts ancestors of these small-bodied apes in India roughly 13 million years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSteroids reduce deaths of critically ill COVID-19 patients, WHO confirms
The finding strengthens evidence that clinicians should give the drugs to people who are severely sick from the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists were trying to develop a low-emission car
Electric cars have surged in popularity, but the vehicles still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyStonehenge enhanced sounds like voices or music for people inside the monument
Scientists created a scale model one-twelfth the size of the ancient stone circle to study its acoustics.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew coronavirus tests promise to be faster, cheaper and easier
Researchers are developing a smorgasbord of tests to detect RNA and proteins from the virus that causes COVID-19.
By Jack J. Lee