Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyEasy interventions like revamping forms help people show up to court
A new study shows that simple behavioral interventions called nudges can help people avoid a missed court appearance and resulting arrest warrant.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyNeandertal babies had stocky chests like their parents
Our evolutionary relatives may have inherited short, deep rib cages from their ancient ancestors.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyBones from an Iron Age massacre paint a violent picture of prehistoric Europe
Bones left unburied, and in one case still wearing jewelry, after a massacre add to evidence that prehistoric Europe was a violent place.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow will Trump’s COVID-19 treatments work together?
Remdesivir, dexamethasone and monoclonal antibodies have individually shown success in clinical trials, but combining them is untested.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHepatitis C discoveries win 2020 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine
The 2020 medicine Nobel recognizes work that found that a novel virus was to blame for chronic hepatitis and led to a test to screen blood donations.
-
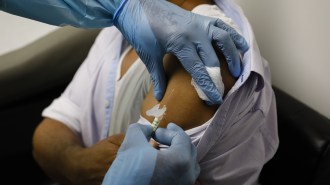 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat does COVID-19 vaccine efficacy mean?
The initial goal for a vaccine against COVID-19 is to reduce cases of the disease by at least 50 percent in those vaccinated versus those not.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNeandertal genes in people today may raise risk of severe COVID-19
People in South Asia and Europe are more likely to carry a genetic heirloom from Neandertals linked to susceptibility to the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, an experimental drug hinted at serotonin’s many roles in the brain
Excerpt from the October 3, 1970 issue of Science News
-
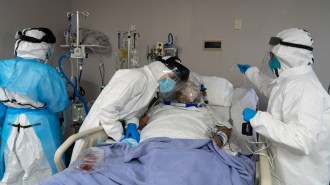 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDefects in early immune responses underlie some severe COVID-19 cases
Scientists are finding that strong early immune responses to the coronavirus are crucial to protect some people from developing life-threatening symptoms.
-
 Space
SpaceA new moon radiation measurement may help determine health risks to astronauts
China's lunar lander measured radiation at the moon’s surface, finding the daily dose is 2.6 times as high as inside the International Space Station.
-
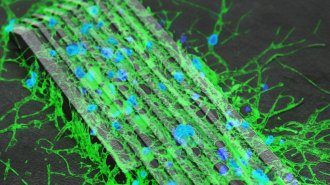 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTiny, magnetically controlled robots coax nerve cells to grow connections
Research using microrobots and nerve cells from rats could point to new treatments for people with nerve injuries.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA Brazilian city devastated by COVID-19 may have reached herd immunity
Up to half of Manaus was infected at the epidemic’s peak, which slowed further spread of the virus but also led to many deaths, scientists say.