
Health & Medicine
‘Smart underwear’ measures how often humans fart
“Zen digesters” rarely fart. “Hydrogen hyperproducers” fart a lot. Scientists are investigating what is typical.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

“Zen digesters” rarely fart. “Hydrogen hyperproducers” fart a lot. Scientists are investigating what is typical.
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.

MRI scans of over 600 Finnish adults found that nearly all had frayed, torn or otherwise abnormal rotator cuffs — yet most had no symptoms.

A “digital gut” predicted which probiotics and high‑fiber diets would take hold in people's guts and produce healthier outcomes.

Teens need eight to 10 hours of sleep each night. A large majority get less than that, according to a national survey of U.S. high school students.
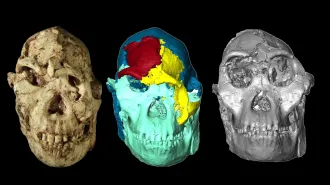
A new digital reconstruction of the face of an early Australopithecus specimen helps add details about the origins of our own species.

Kids with math learning disabilities process number symbols differently than quantities shown as dots — and it shows up in MRIs.

A DNA analysis suggests mosquitoes shifted from nonhuman primates to early humans nearly 2 million years ago.
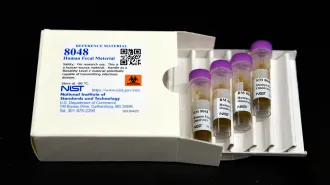
Seven firms reported inconsistent results on the same sample, some over multiple tests. These gut microbe discrepancies could have health consequences.

Fecal analyses and necropsies suggest a fire-footed rope squirrel was the source of a 2023 mpox outbreak among sooty mangabeys in Côte d’Ivoire.

During a test drive, the mobile lab van uncovered a drug-resistant HIV strain that sprung up after the ongoing war with Russia started.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber?
Become one now.