Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn 2019, a ketamine-based antidepressant raised hopes and concerns
Ketamine and related molecules might ease severe depression, but the drugs come with baggage.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaping’s dangers loom large amid more than 50 U.S. deaths this year
Lung injuries and deaths linked to vaping in 2019 are a sobering indication of the dangers of e-cigarettes as teen use continues to rise.
-
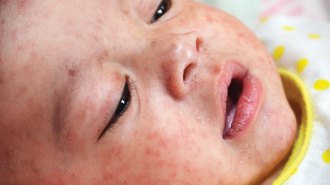 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeasles got a foothold in the United States this year and almost didn’t let go
Areas of low vaccination are blamed for the United States' largest number of measles cases in more than 25 years.
-
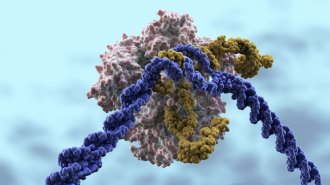 Genetics
GeneticsThe first U.S. trials in people put CRISPR to the test in 2019
Trials of the gene editor in people began in the United States this year, a first step toward fulfilling the technology’s medical promise.
-
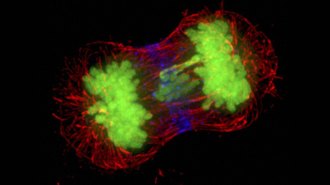 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSurplus chromosomes may fuel tumor growth in some cancers
Extra copies of some genes on excess chromosomes may keep cancer cells growing. Without those extras, cancer cells form fewer tumors in mice.
-
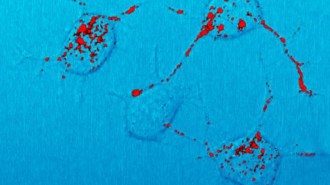 Life
LifePrions clog cell traffic in brains with neurodegenerative diseases
Prions may derail cargo moving inside brain cells, perhaps contributing to cell death in prion diseases.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhy Rembrandt and da Vinci may have painted themselves with skewed eyes
A strongly dominant eye, not an eye disorder, may explain why some great artists painted themselves with one eye turned outward.
By Sofie Bates -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA once-scrapped Alzheimer’s drug may work after all, new analyses suggest
An antibody that targets Alzheimer’s sticky protein amyloid showed promise in slowing mental decline, according to the company that’s developing it.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists’ brains shrank a bit after an extended stay in Antarctica
The experience of an isolated, long-term mission at an Antarctic research station slightly shrunk a part of crew members’ brains, a small study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMedications alone work as well as surgery for some heart disease patients
Patients with stable ischemic heart disease may be able to avoid stents or bypass surgery with medications alone.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIs taking birth control as a teen linked to depression? It’s complicated
As researchers sift through conflicting data, no clear answers emerge on whether birth control during teenage years can cause depression later.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA dose of ketamine could lessen the lure of alcohol
Ketamine may weaken wobbly memories of drinking, a trick that might ultimately be useful for treating alcohol addiction.