Health & Medicine
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNo, the coronavirus wasn’t made in a lab. A genetic analysis shows it’s from nature
Scientists took conspiracy theories seriously and analyzed the coronavirus to reveal its natural origins.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYou can help fight the coronavirus. All you need is a computer
With Folding@home, people can donate computing time on their home computers to the search for a chemical Achilles’ heel in the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen will the coronavirus pandemic and social distancing end?
Social distancing may have to continue for months to prevent a resurgence of COVID-19. Wider testing and isolation of cases could ease such measures.
-
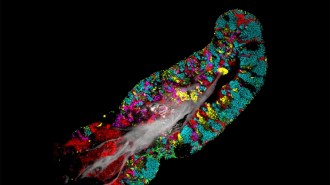 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s where bacteria live on your tongue cells
Scientists labeled bacteria from tongue scrapings with fluorescent probes to glimpse at how the microbes structure their communities.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe number of steps per day, not speed, is linked to mortality rate
Researchers report an association between the total number of steps a person takes each day and the rate of death from any cause.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA tooth-enamel protein is found in eyes with a common form of macular degeneration
Researchers linked a tooth-enamel protein with calcium deposits in eyes suffering ‘dry’ AMD, which could lead to treatments for the vision disorder.
By Alex Fox -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy some heart patients may be especially vulnerable to COVID-19
Researchers don’t yet know if the way the coronavirus enters cells may have something to do with the risks to the heart.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYoung adults can face severe cases of COVID-19, too
While risk of having a severe case of COVID-19 rises with age, younger adults are also landing in the hospital and ICU, new U.S. statistics show.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHIV drugs didn’t work as a coronavirus treatment in a clinical trial
Antiviral HIV drugs “showed no benefit” when given to patients severely ill with COVID-19.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow parents and kids can stay safe and sane during the coronavirus pandemic
Infectious disease experts weigh in on playdates, playgrounds and other parenting questions.
By Laura Sanders and Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists were trying to get a grip on Lassa fever
In 1970, scientists were on the trail of a deadly new virus. Fifty years later, a vaccine is just now being tested in people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePeople who didn’t know they had COVID-19 drove its spread in China
A new study suggests that mild cases, in which people have no symptoms or don’t get sick enough to go to a doctor, are fueling the coronavirus pandemic.