Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMasks help new moms with COVID-19 safely breastfeed their babies
A study reports newborns could be held and breastfed safely when moms with COVID-19 wore masks and cleaned their hands.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo prevent the next pandemic, we might need to cut down fewer trees
Investing in halting deforestation and limiting the wildlife trade could be a cost-effective way to reduce the risk of pandemics, a new analysis finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
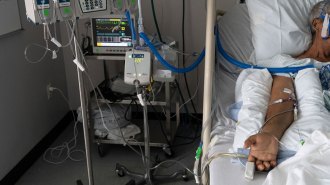
Health & MedicineA blood test may show which COVID-19 patients steroids will help — or harm
An inflammation marker was a good indicator of which patients had lower or higher risks of dying or needing a ventilator when given steroids.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 vaccines by Oxford, CanSino and Pfizer all trigger immune responses
In three clinical trials, vaccine candidates appear safe and induce the production of antibodies and other immune cell responses against the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
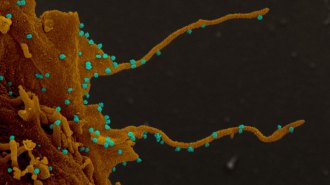
Health & MedicineCoronavirus-infected cells sprout filaments that may spread the virus
Like other coronaviruses, the virus behind COVID-19 causes infected cells to grow spindly projections that may act as highways to other cells.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Space
SpaceWhat will astronauts need to survive the dangerous journey to Mars?
Going to Mars, astronauts will need protections from microgravity and radiation, plus miniature medical devices to diagnose problems and help handle emergencies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRemdesivir may work even better against COVID-19 than we thought
Gilead Sciences says remdesivir cuts the chances of dying from the coronavirus, and data show the drug can curb the virus’s growth in cells and mice.
-
 Health & Medicine
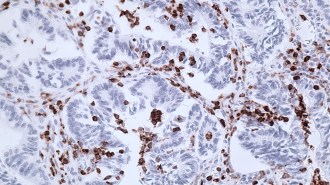
Health & MedicineThese cells slow an immune response. Derailing them could help fight tumors
Immune therapies don’t work for a lot of cancer patients. Some researchers are enhancing these treatments with drugs that stymie suppressor cells.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA COVID-19 vaccine may come soon. Will the blistering pace backfire?
Speed is essential, but not at the expense of safety and efficacy, experts warn. Sacrificing either could damage public trust.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBoosting a liver protein may mimic the brain benefits of exercise
Finding that liver-made proteins influence the brain may advance the quest for an “exercise pill” that can deliver the benefits of physical activity.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThere’s little evidence showing which police reforms work
When stories of police violence against civilians capture public attention, reforms follow despite a dearth of hard data quantifying their impact.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat you need to know about the airborne transmission of COVID-19
More than 200 experts have implored the World Health Organization to acknowledge that the coronavirus can spread through the air.