Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
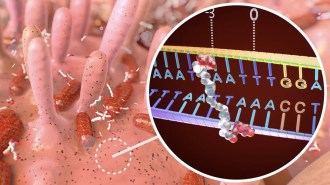
Health & MedicineHow a bacterial toxin linked to colon cancer messes with DNA
A closeup look at colibactin’s structure reveals chemical motifs that guide its mutation-wreaking “warheads” to specific stretches of DNA.
By Elise Cutts -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSelf-hypnosis with cooling mental imagery could ease hot flashes
Postmenopausal women who listened to self-guided hypnosis recordings daily for six weeks saw meaningful improvements in hot flash symptoms.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePersonalized ‘prehabilitation’ helps the body brace for major surgery
A small study finds that individualized prehab can dampen harmful immune responses and may reduce complications after an operation.
By Anna Gibbs -
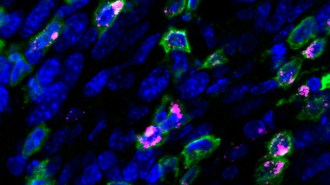 Humans
HumansA therapeutic HPV vaccine shrank cervical tumors in mice
An HPV vaccine delivered into the nose can treat cervical tumors in mice. The vaccine targets a cancer protein produced by the virus.
By Meghan Rosen -
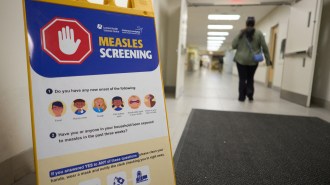 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCanada just lost its measles elimination status. Is the U.S. next?
Canada has had more than a year of continuous measles transmission. The United States has until January to limit cases before losing status.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Butt breathing’ could help people who can’t get oxygen the regular way
Takanori Takebe’s strange investigation into whether humans can use the gut for breathing has surprisingly sentimental origins: helping his dad.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine3,000 steps per day might slow Alzheimer’s disease
In people at risk for Alzheimer’s disease, researchers linked minimal to moderate physical activity to a 3-to 7-year delay in cognitive symptoms.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBuilding a better skin barrier
Skin is a barrier meant to keep small invaders out. Products making their way across it should boost that mission.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA diet low in glutamate may ease migraines
People with Gulf War Illness found relief from migraines after a month on a low-glutamate diet, hinting at a new way to ease symptoms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinemRNA flu vaccines are making their way through clinical trials
The mRNA platform offers the advantage of faster vaccine production, which could allow more time to decide on which flu strains to cover.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn animal tests, this needle-free insulin acted as fast as injections
Managing diabetes with injections is challenging. Joining insulin to a skin-penetrating polymer was as effective as shots at regulating blood sugar.
By Simon Makin -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEroding access to childhood vaccines jeopardizes health for all
Recent U.S. decisions about vaccines signal bigger changes to come that could threaten the foundation of the national childhood immunization schedule.