Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
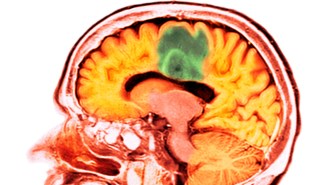
Health & MedicineUltrasound allows a chemotherapy drug to enter the human brain
An early-stage clinical trial demonstrates a technique for getting a powerful chemotherapy drug past the usually impenetrable blood-brain barrier.
-
 Health & Medicine
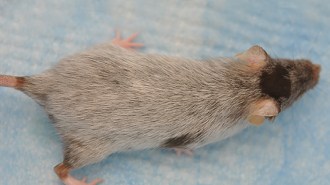
Health & MedicineMouse hair turns gray when certain stem cells get stuck
Stem cells involved in giving hair its color must keep moving and changing maturity levels to prevent graying, a mouse study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFentanyl deaths have spiked among U.S. children and teens
Wider access to naloxone, which reverses the deadly effect of fentanyl, is key as more children are exposed to the opioid, experts say.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we know about upcoming vaccines and antibodies against RSV
New vaccines and monoclonal antibodies may be available this year to fend off severe disease caused by respiratory syncytial virus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePets and people bonded during the pandemic. But owners were still stressed and lonely
People grew closer to their pets during the first two years of COVID. But pet ownership didn’t reduce stress or loneliness, survey data show.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA graphene “tattoo” could help hearts keep their beat
A proof-of-concept electronic heart tattoo relies on graphene to act as an ultrathin, flexible pacemaker. In rats, it treated an irregular heartbeat.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Humans
Humans‘Period’ wants to change how you think about menstruation
Kate Clancy offers fascinating science and history about the uterus and menstruation in her book, Period: The Real Story of Menstruation.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHibernating bears don’t get blood clots. Now scientists know why
People who sit still for hours have an increased risk of blood clots, but hibernating bears and people with long-term immobility don’t. A key clotting protein appears to be the reason why.
-
 Health & Medicine
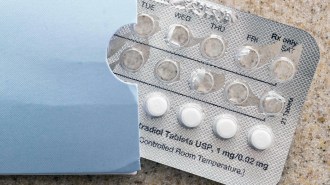
Health & MedicineEstrogen in birth control could be cut way back, a study suggests
Delivering an extra low dose of estrogen, or a combination of estrogen and progesterone, at a specific time of the menstrual cycle may prevent ovulation.
By Natalia Mesa -
 Animals
AnimalsFreshwater leeches’ taste for snails could help control snail-borne diseases
A freshwater leech species will eat snails, raising the possibility that leeches could be used to control snail-borne diseases that infect humans and livestock.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new battery starves cancer cells of oxygen in mice
When a self-charging battery is placed on a mouse’s tumor and combined with anticancer drugs, it reduced tumor size by 90 percent.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe antiviral drug Paxlovid reduces the risk of getting long COVID
In a study of U.S. veterans’ health records, the drug lowered the odds of developing 10 of 13 long-term health problems following a COVID-19 infection.