Health & Medicine
-
 Microbes
MicrobesGut bacteria respect diets, not borders
Malawian and Guahibo gut microbiomes resembled those of herbivorous mammals, while American guts were more similar to carnivores’.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNanoparticle injection blocks breast cancer growth in mice
A nanoparticle-based therapy delivered directly to the mammary ducts could potentially stop pre-cancerous cells from becoming full-blown breast cancer, scientists say.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDistractions raise crash risk for newly licensed drivers
The risk of a crash or near-crash for newly licensed drivers is tripled or greater when they are eating, texting or rubbernecking, researchers report.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVitamin E might limit Alzheimer’s decline
A trial of vitamin E in elderly veterans with Alzheimer’s shows promise for those in the early stages of the disease.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Humans
HumansMother lode
Certain sugar molecules in human breast milk do more to foster beneficial microbes, and banish harmful ones, than they do to nourish newborns.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesThe vast virome
When it comes to the microbiome, bacteria get all the press. But virologists are starting to realize that their subjects also do a lot more than make people sick.
-
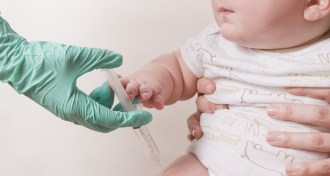 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYear in Review: Putting kids at risk
U.S. parents increasingly are delaying their children’s vaccination.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBad memories fade with a short jolt
Research illustrates the vulnerability of the brain’s information storage.
-
 Humans
HumansNuts in pregnancy may decrease allergy risk in kids
The result runs counter to past studies.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYear in Review: Sleep clears the cluttered brain
Some forms of brain washing are good, like the thorough hosing the brain gets during sleep.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYour youngest kid is three inches taller than you think
Mothers fall prey to the “baby illusion” and consistently underestimate the height of their youngest kid.
-
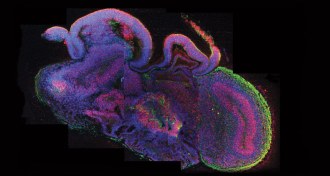 Life
LifeYear in Review: Bioengineers make headway on human body parts
New techniques produce mimics of brain, liver, heart, kidney, retina.
By Meghan Rosen