Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBabies cry at night to prevent siblings, scientist suggests
Babies who demand to be breastfed in the night might be delaying the birth of a sibling, scientist proposes.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBingeing rats show the power of food habits
Rats allowed to binge on sweetened milk show a bad habit for food. But while food might change our habits, a bad food habit may not necessarily be an addiction.
-

-
 Health & Medicine
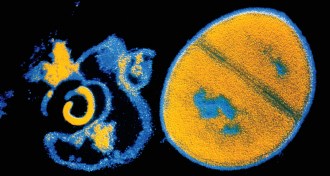
Health & MedicineUnsolved drugs
Long thought to launch precision attacks against bacteria, antibiotics may also cause lethal collateral damage, according to a controversial theory. Exploring how these compounds kill may reveal new ways to fight antibiotic resistance.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGene variant, processed meat linked to boost in cancer risk
In people with a specific variation of a gene on chromosome 10, eating processed meat is associated with an increased risk of developing colon cancer.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEven with rest, brain changes linked to football linger
The offseason may not allow enough time for football players' brains to heal from hard hits.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePossible measles drug tests well in animals
Compound that saves ferrets from viral infection might someday lead to measles treatment.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat’s going on in the mind of a Skyping baby?
By studying how young children respond to video calls, scientists hope to understand the role of new technology.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTriclosan aids nasal invasions by staph
The antimicrobial compound triclosan, commonly found in soaps and toothpaste, may help Staphylococcus aureus stick around.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHepatitis C treatment appears extremely effective
A mix of four medications has provided the most effective way to date to counter the hepatitis C virus in humans.
-
 Computing
ComputingApp could cut jet lag short
A new app calculates lighting schedules to help travelers adjust quickly to new time zones.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeCommon lung infection suffocates with single protein
A Respiratory Syncytial Virus, or RSV, protein creates clumps of dead, bloblike lung cells.
By Beth Mole