Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHealth risks of e-cigarettes emerge
Research uncovers a growing list of chemicals that end up in an e-cigarette user’s lungs, and one study finds that an e-cigarette’s vapors can increase the virulence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
By Janet Raloff -
 Genetics
GeneticsBlind mole-rats are loaded with anticancer genes
Genes of the long-lived blind mole-rat help explain how the animal evades cancer and why it lost vision.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrain’s support cells play role in hunger
Once considered just helpers for neurons, astrocytes sense the hormone leptin and can change mice’s appetites.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYour brain on marijuana: two views
Many of the “facts” that people believe to be true about marijuana are not supported by science, and while the pro-pot lobby cherry-picks data to support its arguments (denying marijuana’s addictiveness, for example), so too do anti-marijuana groups, which play up pot’s dangers.
By Eva Emerson -
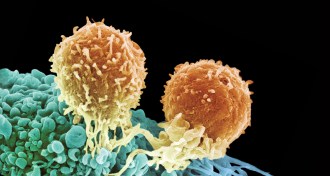 Life
LifeDesigner T cells emerge as weapons against disease
Decades of attempts to boost the immune system’s ability to fight disease are finally starting to pay off. Reprogrammed T cells serve as new weapons against cancer and autoimmune diseases.
By Susan Gaidos -
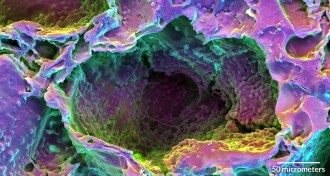 Tech
TechLasers heal damaged rodent teeth
Handheld laser spurs stem cells into action, regrowing dentin in drilled teeth.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSeparating wheat from chaff in gluten sensitivity
Some people who think they are sensitive to gluten might not be after all: Fermentable short chain carbohydrates, or FODMAPs, may be to blame in people with irritable bowel syndrome.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBaby’s first bacteria arrive sooner than we thought
Forget what you’ve heard. The womb is most definitely not sterile.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineUrine is not sterile, and neither is the rest of you
Despite what the Internet says, urine does contain bacteria, a new study finds. And so does your brain, the womb, and pretty much everywhere else.
-
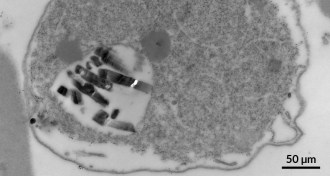 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineParasite protein offers new hope for malaria vaccine
A newly discovered malarial protein triggers the immune system to trap disease-causing parasites in red blood cells. The protein offers scientists a promising target for vaccines.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLife span lengthens when mice feel less pain
When rodents are missing a sensory protein, their metabolism revs up and they live longer.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDengue risk forecasted for soccer World Cup in Brazil
Three Brazilian cities — Recife, Fortaleza and Natal — have the highest risk for outbreaks of dengue fever, according to a new early warning system.