Health & Medicine
-
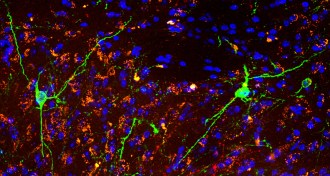
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceShots of brain cells restore learning, memory in rats
Scientists healed damage caused to rats’ brains from radiation by injecting cells that replenish the insulation on neurons.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHandheld device turns smartphone into diagnostic tool
A compact device can process a blood sample to diagnose HIV or syphilis when attached to a smartphone.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineE-cigarettes lower immunity to flu and other germs
Electronic cigarettes produce substantial amounts of lung inflammation, a new mouse study finds. They may also reduce the ability to fight off infections from strep and flu germs.
By Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEven when correct, diagnoses can harm kids
Overdiagnosis is well documented in adults but is often overlooked in children and can lead to unnecessary treatments.
-
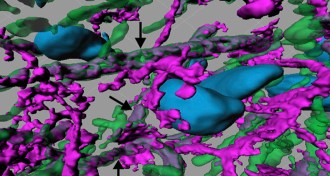
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNewly identified brain circuit could be target for treating obesity
In mice, specific nerve cells control compulsive sugar consumption, but not normal feeding, hinting at a new therapeutic target for treating obesity.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola vaccine performs well in U.K. human trial
A vaccine that protects against the Zaire strain of Ebola turns in promising preliminary results from a human trial.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceImmune system may remember and adapt to stress
Mice without immune systems who receive stressed immune cells are less anxious and more social, suggesting that the immune system can adapt to stress.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureSuperbugs take flight from cattle farms
Winds can carry antibiotics and drug-resistant bacteria from cattle farms to downwind communities.
By Beth Mole -
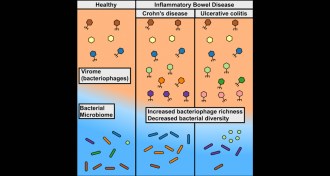 Life
LifeWhen bacteria-killing viruses take over, it’s bad news for the gut
A rise in some bacteria-killing viruses in the intestines may deplete good bacteria and trigger inflammatory bowel diseases.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentAtrazine’s path to cancer possibly clarified
Scientists have identified a cellular button that the controversial herbicide atrazine presses to promote tumor development.
By Beth Mole -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s protective barrier gets leakier with age
Aging influences the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, which may contribute to learning and memory problems later in life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImmune system ‘reset’ may give MS patients a new lease on life
With the help of their own stem cells, MS patients can stop the disease in its tracks in many cases.
By Nathan Seppa