Health & Medicine
-
 Neuroscience
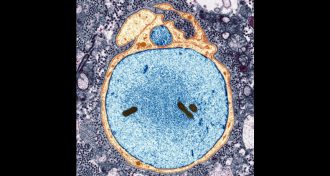
NeuroscienceBrain’s protective barrier gets leakier with age
Aging influences the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, which may contribute to learning and memory problems later in life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImmune system ‘reset’ may give MS patients a new lease on life
With the help of their own stem cells, MS patients can stop the disease in its tracks in many cases.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat’s in a nap? For babies, it may make long-lasting memories
Taking naps after learning seems to help babies less than a year old make memories and keep them, for about a day anyway.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s plumbing may knock out blood test for brain injury
The brain's waste-removal system may complicate scientists' attempts to create a blood test to diagnose traumatic brain injury.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTo beat sleepiness of anxiety drugs, team looks to body’s clock
Studying basic functions, such as the body’s clock, has inadvertently led to a compound that relieves anxiety in mice.
-
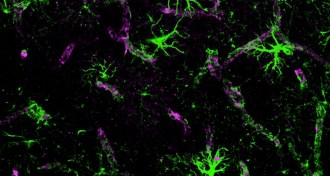
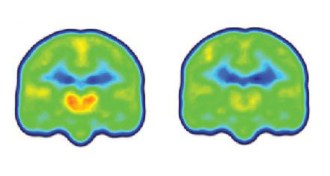 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceProtectors of our nervous system play a role in pain
PET and MRI brain scans show that the cells that protect our central nervous system also play a role in chronic pain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAsthma may add to sleep apnea risk
A long-term sleep study strengthens the link between the two breathing disorders asthma and sleep apnea.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore oxygen may lead to more tumors
Lung cancer risk drops at higher elevations where the air is thinner.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAllergy-related Google searches follow pollen season ups and downs
Google search queries could help researchers track pollen seasons in areas without pollen-monitoring stations.
-
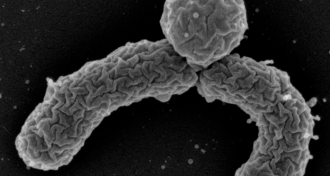 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew antibiotic candidate shows promise
Tests in lab dishes and mice suggest an experimental compound called teixobactin can kill staph, TB microbes and other bacteria.
By Nathan Seppa -
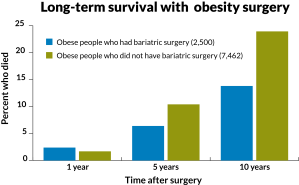 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWeight-loss surgery linked to better survival
Obese middle-aged and older people fare better if they have had bariatric surgery, a long-term study of veterans finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHPV vaccination not linked to multiple sclerosis
Getting vaccinated against human papillomavirus, or HPV, is not associated with developing multiple sclerosis or similar diseases, a new study shows.