Health & Medicine
-
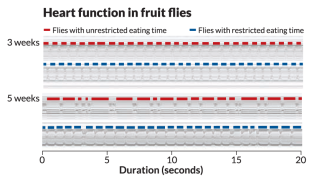 Life
LifeFor healthy eating, timing matters
Limiting eating times improves heart function in fruit flies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRise in measles cases predicted in Ebola-stricken areas
Disruptions in vaccination campaigns in West Africa during the Ebola outbreak could lead to as many as 16,000 deaths from measles in the coming months.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Life
LifeChickens to blame for spread of latest deadly bird flu
Chickens are responsible for the second wave of H7N9 bird flu in China.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTeens have higher anaphylaxis risk than younger kids
Adolescents may be more apt to experience an extreme allergic reaction than younger children, researchers report.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Life
LifeExperimental herpes vaccine works in mice
An experimental herpes vaccine works in animal tests by using an approach starkly different from that used in previous vaccine development.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineArsenic spurs adaptation in Argentinian villagers
The people of San Antonio de los Cobres, Argentina, have genetic adaptations that may help them efficiently get rid of arsenic, a new study shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHepatitis E vaccine shows strong coverage
A large trial in China indicates that a vaccine can provide 87 percent protection against the hepatitis E virus, which infects 20 million people a year.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineReport offers stimulating recommendation on coffee
Results from a committee of experts give the blessing to moderate coffee intake. But as we all raise our mugs, the science behind the report is worth a closer look.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDose of extra oxygen revs up cancer-fighting immune cells
Extra oxygen helps immune cells shrink tumors in cancer-ridden mice.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDespite risks, vaccine delay requests are common
A survey of pediatricians and family doctors finds parents frequently put off vaccines for babies even though doctors warn it can place the children at risk of illness.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSecondhand smoke exposure in womb linked to eczema in childhood
Secondhand smoke exposure in the womb may heighten risk of eczema and other dermatitis in children, a study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Humans
HumansBreast-feeding newborns might limit their allergy to pets later
Breast-feeding newborns might limit their allergy to pets later by inducing a protective mix of gut microbes in the baby.
By Nathan Seppa