Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
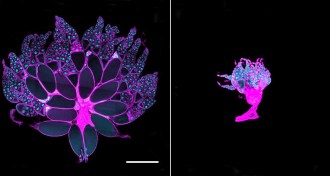
Health & MedicineWhy cancer patients waste away
A tumor-produced protein that interferes with insulin causes wasting in fruit flies with cancer.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNicotine exposure escalates rats’ desire for alcohol
Rats drink more alcohol after they’ve been hooked on nicotine.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenes may influence placebo effect
Certain gene variants may predispose people to experience the placebo effect, which may have implications for clinical trials and personalized medicine.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMarijuana component fights epilepsy
A buzz-free extract of marijuana could help epilepsy patients whose seizures resist other treatments.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThe Angelina effect should be about knowing your cancer risk
Angelina Jolie’s public message about her medical decisions related to cancer is about knowing your risks for disease, not hers.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsContagious cancer found in clams
A soft-shell clam disease is just the third example of a contagious cancer.
-
 Humans
HumansNatural selection may be growing taller Dutch people
Over the past 200 years, natural selection may have driven the evolution of taller Dutch people, researchers posit.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMutation regions mapped on genes that cause breast and ovarian cancer
An analysis of mutated BRCA genes could someday be used for personalized medicine in the fight against breast and ovarian cancer.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrains may be wired to count calories, make healthy choices
Fruit flies appear to make memories of the calories in the food they eat, an observation that may have implications for weight control in humans.
-
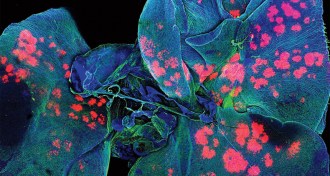 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePink blobs of hope in cancer-targeting quest
Cancer drugs coated with plastic can reach a mouse’s lungs for targeted delivery, but steering the capsules to the right spots can be a challenge.
-
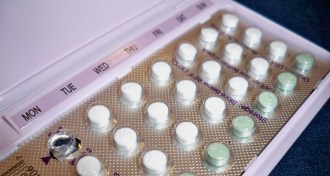 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEarly birth control study probed effectiveness of pill
A 1960s study probed birth control pills’ effectiveness for women. Researchers are still trying to make a pill for men.
-
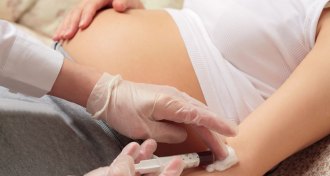 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA more accurate prenatal test to predict Down syndrome
A test to detect genetic problems such as Down syndrome examines a baby’s DNA in the mother’s blood and may limit the need for more invasive screening.