Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTaking antiviral drug ‘on demand’ can guard against HIV
The antiviral drug Truvada taken before and after sex cuts HIV transmission rates.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTaking antiviral drug ‘on demand’ guards against HIV
The antiviral drug Truvada taken before and after sex cuts HIV transmission rates.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Microbes
MicrobesGut microbes signal when dinner is done
Helpful E. coli bacteria that live in the guts of animals produce proteins that can decrease an animal’s appetite only 20 minutes after receiving nutrients
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHaving parasites can boost fertility
Infection with parasitic worms tinkers with fertility.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
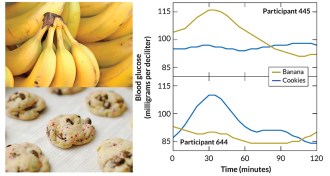
Health & MedicineA good diet for you may be bad for me
Eating the same foods can produce very different reactions in people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEngineered vocal cords show promise in animal tests
Lab-grown vocal cord tissue could lead the way to better treatments for people with vocal problems
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen selenium is scarce, brain battles testes for it
In competition for selenium, testes draw the nutrient away from the brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy brews up more evidence for coffee’s health benefits
Drinking up to five cups of coffee a day reduced the risk of dying early from heart and brain diseases and suicide.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy brews up more evidence for coffee’s health benefits
Drinking up to five cups of coffee a day reduced the risk of dying early from heart and brain diseases and suicide.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNew catalog of human genetic variation could improve diagnosis
Study of human protein-coding variation reveals which genes are more likely to be involved in genetic diseases.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChilly cages may skew disease studies in lab mice
Mice studies on diet and human disease might be marred by stress of cold temperatures in their cages.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceViva vagus: Wandering nerve could lead to range of therapies
Researchers are testing ways to stimulate the vagus nerve to treat a slew of ailments.