Health & Medicine
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOut-of-sync body clock causes more woes than sleepiness
The ailment, called circadian-time sickness, can be described with Bayesian math, scientists propose.
-
 Life
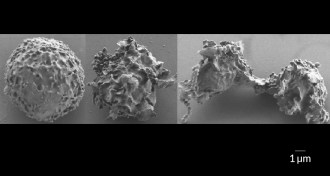
LifePlacenta protectors no match for toxic Strep B pigment
Strep B uses a toxic pigment made of fat to kill immune system cells, spurring preterm labor and dangerous infections, a monkey study shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBaby-led weaning is safe, if done right
Babies who fed themselves solid foods, called baby-led weaning, were no more likely to choke than spoon-fed babies, a new study finds.
-
 Materials Science
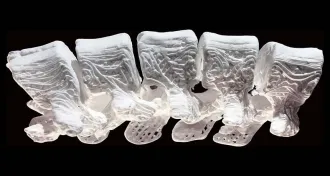
Materials ScienceSuperflexible, 3-D printed “bones” trigger new growth
New ultraflexible material could be the future of bone repair, but awaits human testing.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, noise was a nuisance (it still is)
In 1966, scientists warned of the physical and psychological dangers of a louder world.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDeciphering cell’s recycling machinery earns Nobel
The 2016 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine was awarded to Yoshinori Ohsumi for his work on autophagy, a process that cells use to break down old parts for future use.
By Meghan Rosen and Laurel Hamers -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineJapanese scientist wins Nobel for revealing secrets of cellular recycling
Discovering how cells act as mini recycling plants wins the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine for Japanese cell biologist Yoshinori Ohsumi.
-
 Health & Medicine
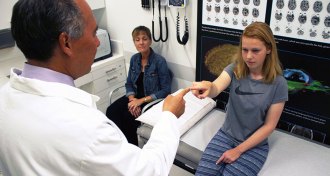
Health & MedicineDon’t cocoon a kid who has a concussion
Parents should fight the urge to limit kids’ activities after a concussion.
-
 Health & Medicine
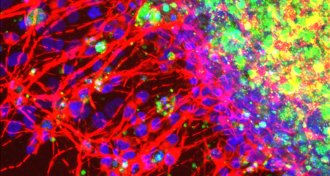
Health & MedicineZika virus infects cells that make bone, muscle in lab tests
Zika virus infects embryonic cranial cells in lab-grown minibrains, potentially altering face and skull shape and brain development, and maybe even contributing to microcephaly.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineConcern expands over Zika birth defects
Infection with Zika virus in utero can trigger a spectrum of birth defects beyond microcephaly, and could potentially cause long-term health problems as well.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsNew case emerging for Culex mosquito as unexpected Zika spreader
The much-debated proposal that a Culex mosquito could help spread Zika gets some international support.
By Susan Milius -
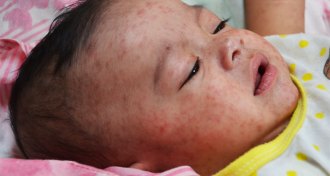 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeasles has been eliminated in the Americas, WHO says
Thanks to wide-spread vaccination against the viral disease, measles has officially been declared eliminated from the Americas.
By Meghan Rosen