Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen should babies sleep in their own rooms?
A new study offers support to sleep-starved parents by suggesting that babies age 6 months and older sleep longer when in their own bedroom.
-
 Health & Medicine
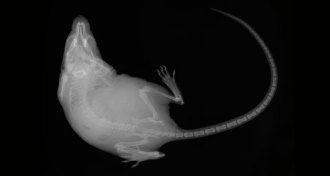
Health & MedicineBones make hormones that communicate with the brain and other organs
Bones send out hormone signals that chat with other parts of the body, studies in mice show. What influence these hormones have in people, though, remain a mystery.
-
 Health & Medicine
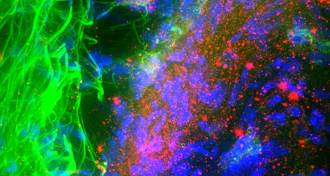
Health & MedicineProtein in Parkinson’s provokes the immune system
The immune system recognizes parts of a protein linked to Parkinson’s disease as foreign, triggering an autoimmune response.
-
 Health & Medicine
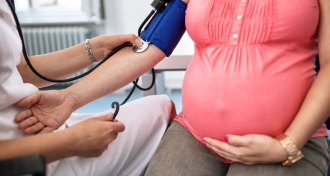
Health & MedicineA baby’s DNA may kick off mom’s preeclampsia
A large genetic analysis points to a protein made by the fetus that may trigger preeclampsia in the mom.
-
 Health & Medicine
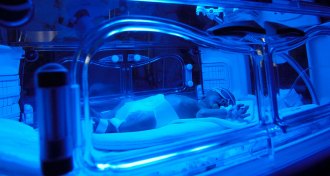
Health & MedicineIn 1967, researchers saw the light in jaundice treatment
Researchers discovered how to use light to treat babies with jaundice 50 years ago. But questions remain about the technique’s effectiveness in some cases.
-
 Health & Medicine
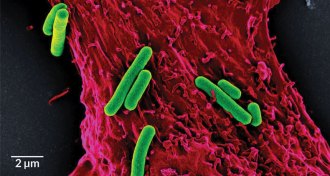
Health & MedicineNew heart attack treatment uses photosynthetic bacteria to make oxygen
Photosynthetic bacteria can produce oxygen to keep rat heart muscles healthy after a heart attack.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew kind of ‘tan in a bottle’ may one day protect against skin cancer
A drug for activating melanin production without using ultraviolet radiation works in human skin samples.
-
 Health & Medicine
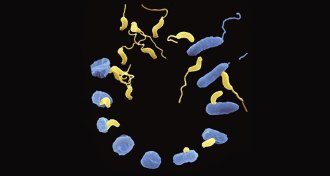
Health & MedicineLive antibiotics use bacteria to kill bacteria
Certain bacteria will destroy other bacteria without harming humans. They may be an answer to antibiotic-resistant infections.
-
 Health & Medicine
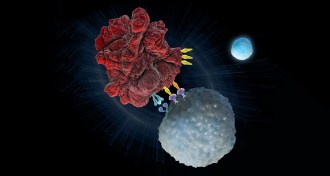
Health & MedicineTherapy flags DNA typos to rev cancer-fighting T cells
Genetic tests help identify cancer patients who will benefit from immune therapy.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIt’s best if babies don’t drink their fruit as juice
New guidelines from the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend no fruit juice for babies younger than 1 year old.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChoosing white or whole-grain bread may depend on what lives in your gut
Gut microbes determine how people’s blood sugar levels respond to breads.
-
 Health & Medicine
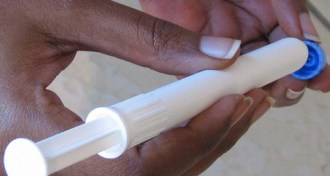
Health & MedicineWhen preventing HIV, bacteria in the vagina matter
Vaginal bacteria affect how well microbicide gels used to prevent HIV work.