Health & Medicine
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhy science still can’t pinpoint a mass shooter in the making
Arguments flare over mass public shootings that remain scientifically mysterious.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsHow oral vaccines could save Ethiopian wolves from extinction
A mass oral vaccination program in Ethiopian wolves could pave the way for other endangered species and help humans, too.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMale birth control pill passes a safety test
A prototype contraceptive for men safely reduced testosterone and other reproductive hormones during a month-long treatment.
-
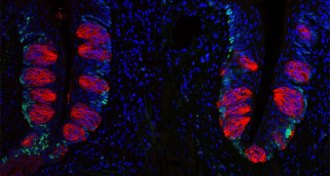 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow obesity makes it harder to taste
Mice that gained excessive weight on a high-fat diet also lost a quarter of their taste buds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHospital admissions show the opioid crisis affects kids, too
Opioid-related hospitalizations for children are up, a sad statistic that shows the opioid epidemic doesn’t just affect adults.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDepression among new mothers is finally getting some attention
Scientists search new mothers’ minds for clues to postpartum depression.
By Laura Beil -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhat we do and don’t know about how to prevent gun violence
Background checks work to prevent gun violence; concealed carry and stand-your-ground laws don’t. But lack of data makes it hard to make other links.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNewer drugs make hepatitis C-positive kidneys safe for transplant
People without hepatitis C did not contract the disease after receiving successful transplants of infected kidneys along with newer antiviral drugs.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceIn the future, an AI may diagnose eye problems
Artificial intelligence could help diagnose blinding eye diseases and other illnesses, speeding up medical care in areas where specialists might be scarce.
-
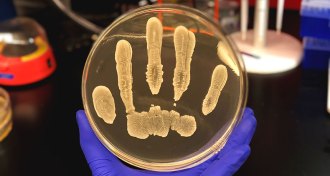 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman skin bacteria have cancer-fighting powers
Strains of a bacteria that live on human skin make a compound that suppressed tumor growth in mice.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesA new way to make bacteria glow could simplify TB screening
A new dye to stain tuberculosis bacteria in coughed-up mucus and saliva could expedite TB diagnoses and drug-resistance tests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen it comes to baby’s growth, early pregnancy weight may matter more than later gains
Women’s weight before and during the first half of pregnancy may be most important indicators of baby’s birth weight.