Health & Medicine
-
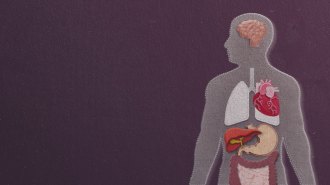 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOrgan age, not just your birthday, may determine your health risks
Blood proteins that reveal some organs age faster than others — and that may predict disease and lifespan.
By Celina Zhao -
 Chemistry
ChemistryGut microbes may flush ‘forever chemicals’ from the body
Experiments in mice show that some gut bacteria can absorb toxic PFAS chemicals, allowing animals to expel them through feces.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThese 5 nutrients might be lacking in your diet
U.S. diets should include more of vitamins D and E, fiber, calcium and magnesium — all are essential nutrients that could offer health benefits.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChronic low back pain may be less likely if you walk – a lot
Adults who walked more than 100 minutes per day were less likely to have chronic low back pain than those who walked fewer than 78 minutes per day.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaccine policy in the U.S. is entering uncharted territory
A key advisory group vows to base decisions on evidence, boost confidence in vaccines and protect health. Experts fear the opposite is happening.
-
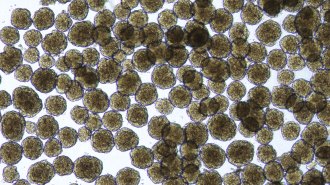 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new diabetes treatment could free people from insulin injections
In a small cell therapy trial, 10 out of 12 people with type 1 diabetes no longer needed supplemental insulin, even a year after treatment.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis painless nanoneedle patch might one day replace certain biopsies
Using millions of tiny needles, the patch samples molecular data from inside cells without damaging them, providing intel on composition in minutes.
By Payal Dhar -
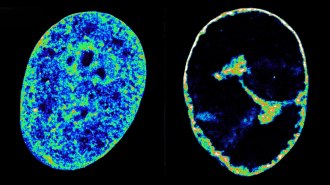 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSee how the herpesvirus reshapes our cells’ DNA in just eight hours
New imaging tools reveal how within an hour of infection, the virus begins to alter our chromosomes to kick-start its own replication.
By Amanda Heidt -
 Climate
ClimateHarmful heat doesn’t always come in waves
Even without reaching heat wave levels, sustained high temperatures may contribute to a litany of health issues.
By Nikk Ogasa -
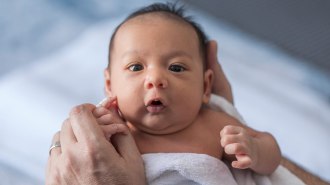 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMany U.S. babies may lack gut bacteria that train their immune systems
Too little Bifidobacterium, used to digest breast milk, in babies' gut microbiomes can increase their risk of developing allergies and asthma.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMailed self-sample kits boosted cervical cancer screening
People who are uninsured or part of a minority racial or ethnic group are underscreened for cervical cancer. Mailing them a self-sample kit may help.
-
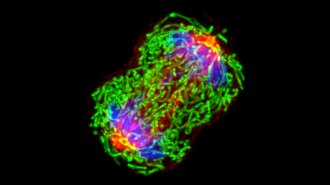 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCancer DNA is detectable in blood years before diagnosis
Tiny, newly formed tumors shed small fragments of DNA that are swept into the bloodstream. Future cancer screening tests could detect them early.
By Meghan Rosen