Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow to help your toddler be helpful (with caveats)
Even very young toddlers like to help, a social skill that’s linked to later success in school and life.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyPhone apps are helping scientists track suicidal thoughts in real time
Researchers are using smartphones to tap into the ups and downs of suicidal thinking that occur over hours and days, hoping to help prevent suicides.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe number of teens who report having sex is down
About 40 percent of high school students are having sex, the lowest amount in the last three decades.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKids with food allergies are twice as likely to have autism
Children with food allergies are more likely to have autism than kids without, a study finds. But that doesn’t mean a child will develop the disorder.
-
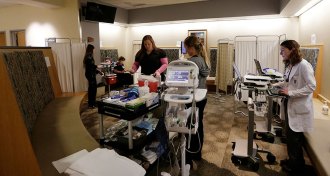 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIf you thought the most recent flu season was bad, you were right
The recent U.S. flu season was classified as highly severe overall, the third time since 2003 that the seasonal outbreak has earned that designation.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSuicide rates have shot up in almost every U.S. state
Suicide rates increased sharply in nearly all 50 states from 1999 to 2016, according to a new government report.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAt-home telomere testing is not a reliable marker of aging, researcher says
Telomere testing for consumers offers a poor measure of “biological age,” says Johns Hopkins oncologist Mary Armanios.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThere are benefits to prenatal yoga, but lingering questions remain
Prenatal yoga offers benefits to pregnant women, but a bigger and more rigorous body of research is needed.
-
 Life
LifeDogs carry a surprising variety of flu viruses
Dogs in China carry a wider variety of flu viruses than previously thought, and may be capable of passing the flu to humans.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat we know — and don’t know — about a new migraine drug
A migraine prevention drug was recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. But some questions about the therapy remain.
-
 Earth
EarthHere’s a look at the world’s deadliest volcanoes — and the ways they kill
Scientists gathered data on nearly 280,000 global volcano deaths from 1500 to 2017 and sorted fatalities by cause of death, such as lava flows or gas.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Outbreak’ puts the life cycle of an epidemic on display
At the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, the exhibit “Outbreak” highlights how infectious diseases shape our world.