Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScared of heights? This new VR therapy could help
Virtual reality may be good training ground for facing your fears in real life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCancer cells engineered with CRISPR slay their own kin
Scientists can program the stealth cells to die before creating new tumors.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyIn research, detours are a key part of discovery
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses the scientific process and the often contradictory research about Alzheimer's disease.
By Nancy Shute -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAir pollution is triggering diabetes in 3.2 million people each year
A new study quantifies the link between smoggy air and diabetes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNo matter their size, newborn stomachs need frequent filling
Studies on newborn stomach size help explain why the tiny humans need to eat so frequently.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEvidence grows that an HPV screen beats a Pap test at preventing cancer
More research finds that a test for human papillomavirus infection catches precancerous cervical cells better than the standard test, a Pap.
-
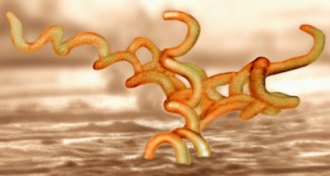 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFinally, there’s a way to keep syphilis growing in the lab
Scientists have figured out how to keep a sample of the bacteria Treponema pallidum alive and infectious for over eight months.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe study of human heredity got its start in insane asylums
‘Genetics in the Madhouse’ reveals how human heredity research began as a statistical science in 19th century insane asylums.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeLeprosy lurks in armadillos in Brazil’s Amazon
Armadillos in the Brazilian Amazon are often infected with leprosy, which they may pass to people.
-
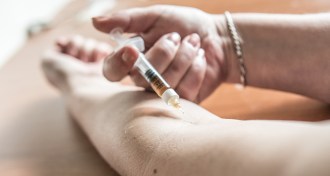 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA brain chemical tied to narcolepsy may play a role in opioid addiction
Long-term use of opioids such as heroin is linked to having more brain cells that release a chemical that regulates wakefulness and arousal.
-
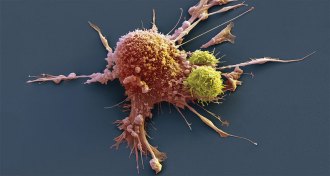 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow to make CAR-T cell therapies for cancer safer and more effective
CAR-T cell therapy was approved by the FDA in late 2017. Now, scientists are working to tame the cancer treatment’s side effects.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMedical breakthroughs come with a human cost
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute muses on the risks many medical advances pose in their infancy.
By Nancy Shute