Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAround the world, reported measles cases jumped 31 percent in 2017
While the number of reported measles cases has dropped 80 percent from 2000 to 2017, high profile outbreaks pushed the 2017 total up from 2016.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKids born in August are diagnosed with ADHD more than kids born in September
August-born kids have higher rates of ADHD diagnosis than kids born in September in U.S. states with a September 1 cutoff for starting kindergarten.
-
 Health & Medicine
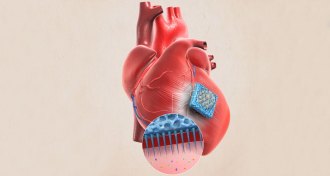
Health & MedicineA patch studded with tiny needles may help heart attack survivors recover
A bandage that sticks to the surface of the heart exudes proteins and other molecules that help muscle cells grow.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMosquitoes may surf winds above Africa more than we realized
More than 40 meters up, balloon traps in Mali caught females of malaria-spreading mosquito species.
By Susan Milius -
 Environment
EnvironmentEngineers are plugging holes in drinking water treatment
Drinking water quality has come a long way in the past hundred years — but challenges remain.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyDo you know how your drinking water is treated?
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses drinking water quality in the United States and the latest research on water treatment technology.
By Nancy Shute -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDon’t spank your kids. Do time-outs and positive talk instead, pediatricians say
A pediatrician group recommends against spanking children — ever — and points instead to positive reinforcement and time-outs to cool off.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSmall doses of peanut protein can turn allergies around
After a year of careful peanut protein exposure, most kids in a clinical trial could tolerate the equivalent of two large peanuts.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFDA restricts the sale of some flavored e-cigarettes as teen use soars
The number of high schoolers who vape rose 78 percent from 2017 to 2018.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLyme and other tickborne diseases are on the rise in the U.S. Here’s what that means.
A record number of tickborne diseases were reported in the United States in 2017. An infectious disease physician discusses that result and others.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCoffee or tea? Your preference may be written in your DNA
Coffee or tea is a bitter choice, a taste genetics study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. cases of a polio-like illness rise, but there are few clues to its cause
A total of 90 cases of acute flaccid myelitis have been confirmed so far this year, out of 252 under investigation.