Genetics
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSource of coffee’s kick found in its genetic code
Coffee doubled up on caffeine-making genes. Those genes evolved independently from similar ones found in tea and chocolate plants.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceSilkworms spin spider-strong threads
Silkworms with a spider protein make silk tough enough to be woven into clothing.
-
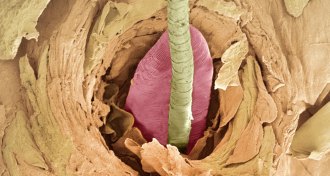 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTiny mites are probably crawling all over your face
Two skin mites, relatives of spiders, might populate the faces of all adult humans, according to a DNA survey.
By Nsikan Akpan -
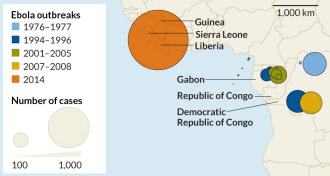 Genetics
GeneticsEbola genome clarifies origins of West African outbreak
Genetic analyses suggest that a single infected person sparked the ongoing Ebola epidemic in West Africa.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAntarctic midge sports tiniest insect genome
Antarctic midge‘s genetic minimalism achieved by skipping a lot of repetitive stretches.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsLong before Columbus, seals brought tuberculosis to South America
Evidence from the skeletons of ancient Peruvians shows that seals may have brought tuberculosis across an ocean from Africa.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDebate rages over mouse studies’ relevance to humans
Last year, researchers said rodents are not good mimics of human inflammation; a new study says the reverse.
-
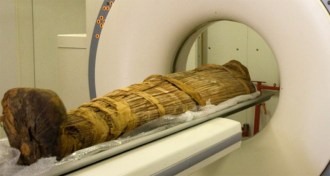 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMummies reveal hardened arteries
Mummy studies suggest heart disease is an ancient malady, not just the product of modern diets and sedentary lifestyles.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene activity change can produce cancer
Scientists have long thought that epigenetic changes, which alter gene activity, can cause cancer. Now they have demonstrated it in a mouse experiment.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAirborne MERS virus found in Saudi Arabian camel barn
The air in a Saudi Arabian camel barn holds genetic fragments of MERS, a new study shows.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHints about schizophrenia emerge from genetic study
From thousands of genomes, researchers pinpoint dozens of DNA changes that may underlie schizophrenia
-
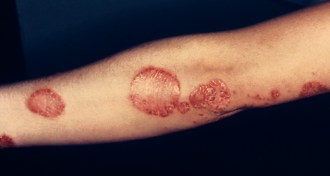 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTwo genes clear up psoriasis and eczema confusion
Psoriasis and eczema are often mistaken for each other, leading to mistreatment. Testing just two genes could eliminate this confusion.
By Nsikan Akpan