Genetics
-
 Life
LifeAneil Agrawal unites math and mess
Evolutionary geneticist Aneil Agrawal is equally at home with real and hypothetical fruit flies.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsTo study Galápagos cormorants, a geneticist gets creative
To collect DNA from four cormorant species, this scientist called in bird scientists far and wide.
-
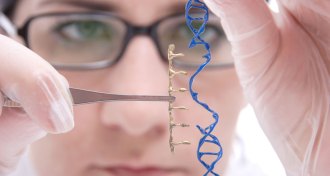 Genetics
GeneticsGenetic surgery is closer to reality
A molecular scalpel called CRISPR/Cas9 has made gene editing possible.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTasmanian devils evolve resistance to contagious cancer
Tasmanian devils are evolving resistance to a deadly contagious cancer.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes help snub-nosed monkeys live the high life
Snub nosed monkeys have certain genetic variants that help them breathe easy in low oxygen.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThank (or blame) your genes for ability to handle java jolt
A gene involved in caffeine processing may control coffee consumption.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesBacteria display qualities that a mother would love
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses big lessons we can learn from some of Earth's smallest organisms.
By Eva Emerson -
 Life
LifeCRISPR inspires new tricks to edit genes
CRISPR/Cas9 has been a rockstar gene-editing tool for just four years and it’s already being tweaked to do more things better.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDarwin’s Dogs wants your dog’s DNA
The Darwin’s Dogs citizen science project is collecting canine DNA to better understand dog genetics and behavior.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHow to get Ötzi’s look
DNA from Ötzi the Iceman’s clothes and quiver traced to both domesticated and wild animals.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsGenetic diversity data offers medical benefits
Study of protein-producing DNA narrows down disease-causing genetic variants.
-
 Life
LifeGenes that control toxin production in C. difficile ID’d
Pinpointing the genes behind Clostridium difficile toxin production could help researchers disarm the superbug without killing “good” bacteria.