Genetics
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA recount of human genes ups the number to at least 46,831
A new estimate of the number of human genes adds in some RNA-producing genes.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGerman skeletons hint that medieval warrior groups recruited from afar
Graveyard finds may come from an ancient European warrior household with political pull.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTeens born from assisted pregnancies may have higher blood pressure
Kids born from reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization are susceptible to high blood pressure as adolescents, a small study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCRISPR gene editing relieves muscular dystrophy symptoms in dogs
Scientists have used CRISPR’s molecular scissors in beagle puppies to repair a genetic mutation that causes muscular dystrophy.
-
 Humans
HumansMeet the first known child of a Neandertal and a Denisovan
DNA analysis of a bone fragment reveals Neandertal movements between Siberia and western Europe.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAmericans support genetically engineering animals for people’s health
Genetically engineering animals is OK with Americans if it improves human health, a new poll reveals.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA resurrected gene may protect elephants from cancer
Researchers have found another gene that may play a role in explaining elephants’ cancer resistance.
-
 Life
LifeTiny bits of RNA can trigger pain and itchiness
Two microRNAs may shed light on the causes of nerve pain and itch.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe first gene-silencing drug wins FDA approval
The FDA just approved the first drug that works via RNA interference.
-
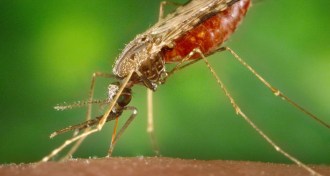 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA newly approved drug could be a boon for treating malaria
Tafenoquine could help prevent the recurring form of malaria, but the drug may also be dangerous for people who have a certain genetic mutation.
-
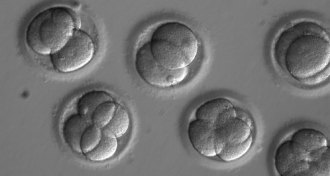 Genetics
GeneticsResearchers say CRISPR edits to a human embryo worked. But critics still doubt it
Researchers say that they have confirmed CRISPR/Cas9 edits of a heart disease–causing version of a gene, but critics still have doubts.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThe debate over people’s pathway into the Americas heats up
Defenders of an ice-free inland passage for early Americans make their case.
By Bruce Bower