Genetics
-
 Genetics
GeneticsPlague may have caused die-offs of ancient Siberians
DNA suggests that the deadly bacterium that causes the plague reached northeast Asia by 4,400 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow some ticks protect themselves from deadly bacteria on human skin
A gene that ticks acquired from bacteria 40 million years ago may help the arachnids keep potential pathogens at bay while feeding on blood.
-
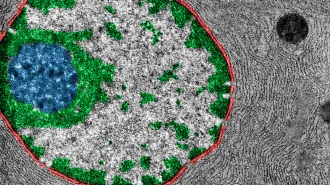 Genetics
GeneticsA key to the mystery of fast-evolving genes was found in ‘junk DNA’
A new study challenges a long-held belief that essential genes change little over time.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsPenicillin allergies may be linked to one immune system gene
Researchers have located a shared hot spot — on the HLA-B gene — in the immune system in people who say they have penicillin allergies.
-
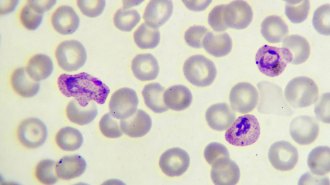 Microbes
MicrobesHow malaria parasites hide from the human immune system
By turning genes on or off, the parasite keeps blood levels low but persistent, so infection doesn’t set off alarm bells for the immune system.
-
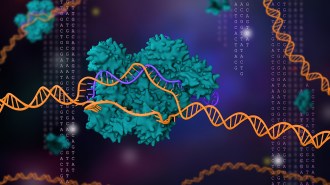 Genetics
GeneticsGene-editing tool CRISPR wins the chemistry Nobel
A gene-editing tool developed just eight years ago that has “revolutionized the life sciences” nabbed the 2020 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHepatitis C discoveries win 2020 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine
The 2020 medicine Nobel recognizes work that found that a novel virus was to blame for chronic hepatitis and led to a test to screen blood donations.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsStrict new guidelines lay out a path to heritable human gene editing
But scientists say making changes in DNA that can be passed on to future generations still isn’t safe and effective, yet.
-
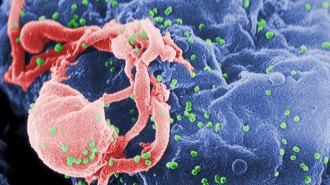 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn a first, a person’s immune system fought HIV — and won
Some rare people may purge most HIV from their bodies, leaving only broken copies of the virus or copies locked in molecular prisons, from which there is no escape.
-
 Life
LifeClimate change, not hunters, may have killed off woolly rhinos
Ancient DNA indicates that numbers of woolly rhinos held steady long after people arrived on the scene.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsHow tuatara live so long and can withstand cool weather
Tuatara may look like your average lizard, but they’re not. Now, researchers have deciphered the rare reptiles’ genome, or genetic instruction book.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsAn immune system quirk may help anglerfish fuse with mates during sex
Deep-sea anglerfish that fuse to mate lack genes involved in the body’s response against pathogens or foreign tissue.