Genetics
-
 Genetics
Genetics‘The Code Breaker’ tells the story of CRISPR pioneer Jennifer Doudna
In his latest book, Walter Isaacson chronicles the discovery of CRISPR and delves into the ethics of gene editing.
-
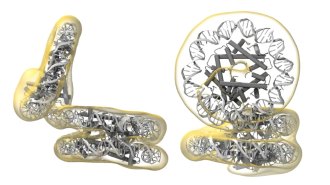 Microbes
MicrobesArchaea microbes fold, twist and contort their DNA in extreme ways
Single-celled archaea open and close their Slinky-like genetic material in a clamshell motion, possibly providing easy access to their genes.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA databases are too white, so genetics doesn’t help everyone. How do we fix that?
A lack of diversity in genetic databases is making precision medicine ineffective for many people. One historian proposes a solution: construct reference genomes for individual populations.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe first human genetic blueprint just turned 20. What’s next?
The Human Genome Project led to many medical advances. Deciphering 3 million African genomes and using new tech to fill gaps could lead to even more.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome Neandertal genes in people today may protect against severe COVID-19
Neandertal DNA on chromosome 12 may affect genes involved in a biochemical chain reaction that ends with the destruction of viral RNA.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe oldest animal DNA ever recovered reveals mammoths’ evolution
Mammoths evolved to handle the cold over hundreds of thousands of years and North America may been home to a hybrid species, a new study finds.
-
 Plants
PlantsModified genes can distort wild cotton’s interactions with insects
In a Yucatan nature park, engineered genes influence nectar production, affecting ants’ and maybe pollinators’ attraction to the wild cotton plants.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsLizard-like tuatara carry two distinct mitochondrial genomes
Having two mitochondrial genetic instruction books, a first for vertebrates, may help explain tuatara’s unique ability to tolerate cold temperatures.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSome identical twins don’t have identical DNA
Mutations arising early in development may account for genetic differences between identical twins.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsPlague may have caused die-offs of ancient Siberians
DNA suggests that the deadly bacterium that causes the plague reached northeast Asia by 4,400 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow some ticks protect themselves from deadly bacteria on human skin
A gene that ticks acquired from bacteria 40 million years ago may help the arachnids keep potential pathogens at bay while feeding on blood.
-
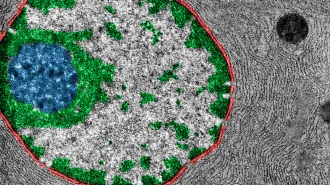 Genetics
GeneticsA key to the mystery of fast-evolving genes was found in ‘junk DNA’
A new study challenges a long-held belief that essential genes change little over time.