Genetics
-
 Life
Life‘Life as We Made It’ charts the past and future of genetic tinkering
A new book shatters illusions that human meddling with nature has only just begun.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesAre viruses alive, not alive or something in between? And why does it matter?
The way we talk about viruses can shift scientific research and our understanding of evolution.
-
 Life
LifeGene-edited stem cells help geckos regrow more perfect tails
Regenerated gecko tails are a far cry from perfect. Now experiments have coaxed geckos to regrow better ones with nerve tissue and bonelike cartilage.
By Freda Kreier -
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA from mysterious Asian mummies reveals their surprising ancestry
Ancient DNA indicates that an enigmatic Bronze Age group consisted of genetic, but not cultural, loners.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDog DNA reveals ancient trade network connecting the Arctic to the outside world
People in Siberia were exchanging canines and probably other goods as early as 7,000 years ago with cultures as far off as Europe and the Near East.
By Freda Kreier -
 Genetics
GeneticsAll identical twins may share a common set of chemical markers on their DNA
Identical twins may share a set of unique chemical tags on their DNA that could be used to identify individuals who were conceived as identical twins.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA offers a new look at how Polynesia was settled
Modern genetic evidence suggests that statue builders on islands such as Rapa Nui, also known as Easter Island, had a shared ancestry.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient DNA shows the peopling of Southeast Asian islands was surprisingly complex
Ancient DNA from a hunter-gatherer skeleton points to earlier-than-expected human arrivals on Southeast Asian islands known as Wallacea.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsAn Indigenous people in the Philippines have the most Denisovan DNA
Genetic comparisons crown the Indigenous Ayta Magbukon people as having the most DNA, 5 percent, from the mysterious ancient hominids.
By Bruce Bower -
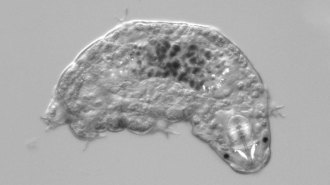 Life
LifeNear-invincible tardigrades may see only in black and white
A genetic analysis suggests that water bears don’t have light-sensing proteins to detect ultraviolet light or color.
-
 Humans
HumansOnly a tiny fraction of our DNA is uniquely human
Some of the exclusively human tweaks to DNA may have played a role in brain evolution.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOne mutation may have set the coronavirus up to become a global menace
A study pinpoints a key mutation that may have put a bat coronavirus on the path to becoming a human pathogen, helping it better infect human cells.