Environment
-
 Climate
ClimateRivers may gush under sullied skies
By dimming sunlight and curbing evaporation, air pollution can increase the amount of water flowing through rivers, new simulations suggest.
By Beth Mole -
 Environment
EnvironmentWorld’s first full-scale clean coal plant now up and running
After decades of delays, technology that cuts carbon emissions from commercial power plants has made its worldwide debut.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentHuman ingenuity takes on Mother Nature in ‘The Big Ratchet’
Geographer Ruth DeFries explains how technological innovations have allowed humans to overcome environmental challenges throughout history.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCrops take up drugs from recycled water
Plants irrigated with recycled wastewater can soak up tiny amounts of pharmaceutical compounds but what this means for human health is unclear.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateGreenhouse gases reached new records in 2013
Levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere rose more last year than any other year since 1984, according to a September 9 report by the World Meteorological Organization.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceGreener water splitter for hydrogen fuel designed
A new gadget that runs on a single AAA battery might truly reduce the carbon emissions from hydrogen fuel cell production down to zero.
-

-
 Environment
EnvironmentCarbon capture and storage finally approaching debut
Carbon capture and storage offers a way to rein in global carbon emissions. But financial and regulatory obstacles, as well as public fears, are delaying the technology’s long-awaited implementation.
By Beth Mole -
 Environment
EnvironmentFetuses may be exposed to antimicrobial compounds
Health risks remain uncertain as scientists find common soap chemicals in pregnant women and cord blood.
By Beth Mole -
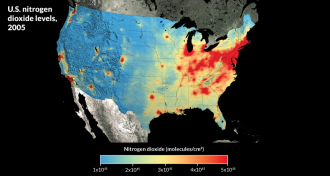 Environment
EnvironmentUps and downs in the quest for clean air
Satellite views reveal good news on U.S. air pollution trends.
By Andrew Grant -
 Oceans
OceansMercury at ocean surface may have tripled since preindustrial times
Questions remain over dangers of toxic metal in environment.
By Beth Mole -
 Environment
EnvironmentDeepwater Horizon damage footprint larger than thought
In the Gulf of Mexico, most deep-sea corals have escaped damage from the Deepwater Horizon blowout. However, the impact does extend deeper and wider than previously thought.