Environment
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureGrapevines are more drought-tolerant than thought
Grapevines handle drought better than previously thought. This could inform irrigation management.
By Dan Garisto -
 Earth
EarthGassy farm soils are a shockingly large source of these air pollutants
California’s farm soils produce a surprisingly large amount of smog-causing air pollutants.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentPlastic pollution increases risk of devastating disease in corals
Researchers estimate about 11 billion pieces of plastic are polluting Asia-Pacific corals, raising the risk of disease at scores of reefs.
By Dan Garisto -
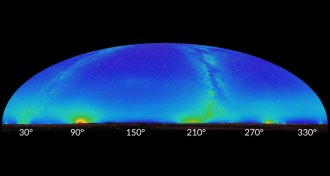 Astronomy
AstronomyPollution is endangering the future of astronomy
Astronomers discuss multiple threats from pollution that will make it harder to observe the night sky.
By Dan Garisto -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFracking linked to low birth weight in Pennsylvania babies
Babies born to moms living within one kilometer of a hydraulic fracturing site were more likely to be born underweight, researchers say.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWorries grow that climate change will quietly steal nutrients from major food crops
Studies show that rice, wheat and other staples could lose proteins and minerals, putting more people at risk of hunger worldwide.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsSeeds coated in a common pesticide might affect birds’ migration
Eating small amounts of a neonicotinoid pesticide can disorient white-crowned sparrows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEven a tiny oil spill spells bad news for birds
Just a small amount of crude can make birds less active.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe key to breaking down plastic may be in caterpillars’ guts
Caterpillars that feast on plastic have different gut microbes than those that eat a grain-based diet.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentPollution killed 9 million people in 2015
First global look estimates the massive human and financial toll caused by pollution-related health problems.
By Laura Beil -
 Chemistry
ChemistryChong Liu one-ups plant photosynthesis
Chong Liu mixes bacteria and inorganics into systems that can generate clean energy better than a leaf.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentRadioactive material from Fukushima disaster turns up in a surprising place
Radioactive cesium is reaching the ocean through salty groundwater.