Ecosystems
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsVirus-blocking insects taking over Vietnamese island
Field trial tests mosquitoes that may stop the spread of dengue infection.
By Beth Mole -

-
 Life
LifeMorel mushroom may grow crop of its own
A fungus could be a farmer itself, sowing, cultivating and harvesting bacteria.
By Susan Milius -

-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsFeces in termites’ nests block biological pest control
Built-in poop nourishes bacteria that protect notorious Formosan species.
By Susan Milius -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsAging European forests full to the brim with carbon
Trees' capacity to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is dwindling.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaur had impressive schnoz
Fossils found in Utah reveal geographic segregation of horned species.
By Erin Wayman -
 Plants
PlantsMosses frozen in time come back to life
Buried under a glacier for hundreds of years, plants regrow in the lab.
By Erin Wayman -
 Life
LifeMicrobes flourish at deepest ocean site
At the bottom of the Mariana Trench, eleven kilometers down, bacteria prosper despite crushing pressure and isolation.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNative pollinators boost crop yields worldwide
Farms with crops from coffee to mangoes don’t get the best yields if they rely solely on honeybees.
By Susan Milius -
 Humans
HumansU.S. team breaks through subglacial lake
Testing should continue for a day or more, probing for life in the Antarctic depths.
By Janet Raloff -
 Life
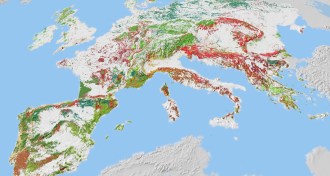
LifeVictorian zoological map redrawn
Species distribution patterns that inspired Darwin and Wallace get an update.
By Susan Milius