Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Earth
EarthFossil mimics may be more common in ancient rocks than actual fossils
Evidence of early life may be harder to preserve than pseudofossils — structures that form abiotically but resemble living remnants.
-
 Earth
EarthThe birth of a lightning bolt was caught on video
High-speed imagery shows the formation of an electrical connection between opposing currents, offering new insight into how these flashes form.
-
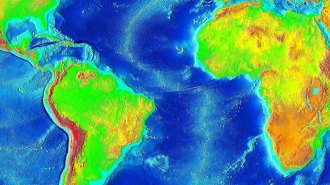 Earth
EarthAn upwelling of rock beneath the Atlantic may drive continents apart
Rock rising from more than 600 kilometers deep at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge may play a more active role in plate tectonics than thought.
-
 Climate
ClimateShip exhaust studies overestimate cooling from pollution-altered clouds
Lines of clouds formed by ship exhaust offer a window into aerosol-cloud interactions but may overestimate how much pollution-altered clouds cool the climate.
-
 Climate
ClimateHow much will Africa capitalize on cheap renewable energy as its power grid grows?
An analysis of the successes and failures of past electrical power projects across Africa suggests the continent isn’t likely to go green before 2030.
-
 Earth
EarthSpace station detectors found the source of weird ‘blue jet’ lightning
The origins of an enigmatic type of lightning in the upper atmosphere has been traced to a 10-microsecond flash of bright blue light.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome bacteria are suffocating sea stars, turning the animals to goo
For years, researchers thought an infectious pathogen was behind sea star wasting disease. Instead, bacteria deplete the starfishes’ oxygen.
-
 Climate
Climate‘The New Climate War’ exposes tactics of climate change ‘inactivists’
In his new book, climate scientist Michael Mann draws the battle lines for a new phase of the struggle against climate change denialism.
-
 Climate
Climate2020 and 2016 tie for the hottest years on record
Ocean temperature data as well as temperatures measured over land at weather stations around the globe revealed the extent of the warming.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyMarie Tharp’s groundbreaking maps brought the seafloor to the world
In part because of her gender, Tharp was the right person in the right place at the right time to make the first detailed maps of the ocean’s bottom.
By Betsy Mason -
 Earth
EarthHow the Earth-shaking theory of plate tectonics was born
Plate tectonics explains many of Earth’s geologic wonders and natural hazards — and may hold clues to the evolution of life.
-
 Earth
EarthEarth’s oceans are storing record-breaking amounts of heat
2020 was just the latest in a series of record-breaking years for ocean heat.