Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Climate
ClimateCanada’s Crawford Lake could mark the beginning of the Anthropocene
The mud of a Canadian lake holds an extremely precise record of humans’ influence on Earth. But the Anthropocene isn’t an official geologic epoch yet.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceThis ‘thermal cloak’ keeps spaces from getting either too hot or cold
A new thermal fabric prototype could help keep cars, buildings and other spaces a comfortable temperature during heat waves while reducing CO₂ emissions.
By Skyler Ware -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsThis seagrass is taking over the Chesapeake Bay. That’s good and bad news
Higher water temperatures are wiping out eelgrass in the Chesapeake Bay and weedy widgeongrass is expanding. Here’s why that seagrass change matters.
By John Carey -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis ancient, Lovecraftian apex predator chased and pierced soft prey
Half a billion years ago, Anomalocaris canadensis probably used its bizarre headgear to reach out and snag soft prey with its spiky clutches.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Chemistry
ChemistryTear-resistant rubbery materials could pave the way for tougher tires
Adding easy-to-break molecular connectors surprisingly makes materials harder to tear and could one day reduce microplastic pollution from car tires.
By Skyler Ware -
 Climate
ClimateAntarctic sea ice has been hitting record lows for most of this year
Since hitting a record low minimum back in February, the amount of Antarctic sea ice has stayed well below normal all year.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDust from a shrinking Great Salt Lake may be accelerating Utah’s snowmelt
About a quarter of the record-breaking, snow-melting dust on the Wasatch Mountains in 2022 may have come from exposed lakebed at Great Salt Lake.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe snow forest of North America may be about to shrink
From 2000 to 2019, the boreal forest’s northern boundary didn’t move while southern tree cover thinned due to climate change, wildfires and logging.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Earth
EarthIrrigation may be shifting Earth’s rotational axis
Computer simulations suggest that from 1993 to 2010 irrigation alone could have nudged the North Pole by about 78 centimeters.
By Sid Perkins -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsThe Amazon might not have a ‘tipping point.’ But it’s still in trouble
Scientists race to foretell the fate of the vast forest facing deforestation and climate change.
By Nikk Ogasa -
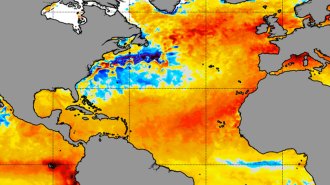 Climate
ClimateWhy is the North Atlantic breaking heat records?
Record-breaking sea-surface temperatures off the coast of Africa may affect the 2023 hurricane season. What’s fueling the unusual heat is unclear.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsCamouflaging wheat with a wheat smell could be a new approach to pest control
Wheat fields coated in wheat germ oil confuse the noses of mice, reducing seed loss by more than 60 percent, a new study finds.