Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Climate
ClimateGreenhouse gases may spell wet future for Africa
Greenhouse gases played a role in boosting rainfall in Africa 14,000 to 21,000 years ago, a finding that may help predict future abundance of water on the continent.
By Beth Mole -

-
 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePreparing for disaster, celebrating success
Science cannot prevent all disasters or solve all the problems they spawn, but it can point to the best ways to prepare, making disasters less damaging than they might otherwise be
By Eva Emerson -
 Earth
EarthStudying a volcano in a war zone
New isotope analyses offer bad news for the people of Goma, a burgeoning city in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: Mount Nyiragongo may be more dangerous than expected.
-
 Earth
EarthExhibit lays out principles for disaster-resistant structures
The National Building Museum’s ‘Designing for Disaster’ exhibit showcases the science and engineering of making disaster-resistant infrastructure.
By Erin Wayman -
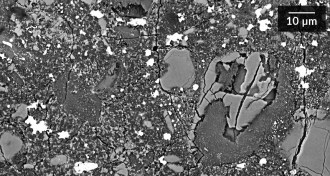 Earth
EarthEarth’s most abundant mineral finally has a name
Bridgmanite, the planet’s most common mineral, christened after traces found in 1879 meteorite.
-
 Oceans
OceansRobotic subs reveal thicker Antarctic sea ice
New measurements by robotic subs suggest that scientists have underestimated Antarctic sea ice thickness.
-
 Earth
Earth‘Mass Extinction’ vivifies the science of die-offs
The dinosaurs were killed off some 65 million years ago after a colossal asteroid struck Earth. But what many people probably don’t know is how paleontologists came to that conclusion. "Mass Extinction: Life at the Brink" tells that story.
By Erin Wayman -
 Animals
AnimalsScientists’ tags on fish may be leading seals to lunch
In an experiment, 10 young grey seals learned to associate the sound of a pinging tag with fish. The tags may make fish vulnerable to predators, scientists say.
-
 Life
LifeTasty animals end up on latest list of threatened species
Growing food market lands several species, including Pacific bluefin tuna and Chinese pufferfish, on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDDT lingers in Michigan town
Decades after a plant manufacturing DDT shut down in Michigan, the harmful insecticide is still found in neighboring birds and eggs.
By Beth Mole -
 Environment
EnvironmentColorado deluge produced flood of drug-resistance genes
Flooding in Colorado’s South Platte River Basin washed antibiotics and drug-resistance genes into pristine waterways.
By Beth Mole