Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Earth
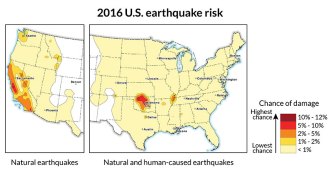
EarthQuake risk in parts of central U.S. as high as in fault-filled California
A new report from the U.S. Geological Survey shows an increased earthquake hazard from human activities such as the disposal of fracking wastewater.
-
 Climate
ClimateMaximum size for Arctic sea ice hits a new low
Warm temperatures helped drop the Arctic sea ice maximum to the smallest size on record.
-
 Earth
EarthBeware of rockfalls in warm weather
Cracks in cliff faces grow and shrink as temperatures warm and cool, new research shows.
-

-
 Climate
ClimateOrganic molecules help fatten cloud-making water droplets
Cloud-forming water droplets can grow larger thanks to organic molecules on the exterior of the drop, new research suggests.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureReaders debate GMOs
Genetically-modified food, nuclear fusion, black holes and more reader feedback.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureClimate change threatens quality of French, Swiss wines
Wine quality could suffer as climate change desynchronizes warm temperatures and droughts, preventing grape growers from harvesting at the optimum time.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureWine quality subject to climate change
Wine quality could suffer as climate change desynchronizes warm temperatures and droughts, preventing grape growers from harvesting at the optimum time.
-
 Earth
EarthCO2 shakes up theory of how geysers spout
Carbon dioxide helps fuel eruptions of Spouter Geyser, and perhaps other features, in Yellowstone National Park, new research suggests.
-
 Climate
ClimateAntarctic history suggests ice sheet ‘danger’ threshold
Carbon dioxide levels during the Antarctic ice sheet’s formation 34 million years ago suggest that Earth could soon enter “danger zone” for ice sheet’s demise.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsFinding wonders in fat
In the latest issue of Science News, Editor in Chief Eva Emerson talks fat cells, thermodynamics, and lead poisoning.
By Eva Emerson -
 Oceans
OceansSwirls of plankton decorate the Arabian Sea
The dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans is taking over in the Arabian Sea, posing a potential threat to its ecosystem.