Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Climate
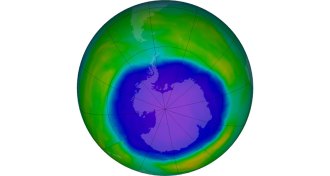
ClimateDespite volcanic setback, Antarctic ozone hole healing
The September extent of the Antarctic ozone hole has shrunk by about 4.5 million square kilometers since 2000, thanks in large part to the Montreal Protocol.
-
 Climate
ClimateWorld will struggle to keep warming to 2 degrees by 2100
Current plans to curb climate change aren’t ambitious enough to limit global warming below 2 degrees Celsius by 2100, new research shows.
-
 Earth
EarthWinning helium hunt lifts hopes element not running out
A volcanic region of Tanzania contains more than a trillion liters of helium gas, enough to fill 1.2 million medical MRI scanners — or hundreds of billions of balloons, researchers report.
-
 Oceans
OceansCoral bleaching event is longest on record
Widespread coral bleaching continues, in the longest episode, over the largest area to date.
-
 Oceans
OceansDeep-sea hydrothermal vents more abundant than thought
Ecosystem-supporting hydrothermal vents are much more abundant along the ocean floor than previously thought.
-
 Space
SpaceReaders weigh in on ET and the meaning of life
Reader feedback from the June 25, 2016, issue of Science News
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceLong-lost ‘extinct’ meteorite found
A newly discovered meteorite, nicknamed Öst 65, may have originated from the same collision that formed L chondrites, one of the most abundant groups of meteorites on Earth.
-
 Earth
EarthA third of the population can’t see the Milky Way at night
Light pollution conceals the Milky Way’s star-spangled core from more than a third of Earth’s population, a global atlas of artificial sky luminance reveals.
-
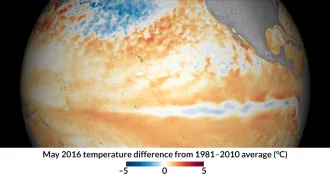 Climate
ClimateThe ‘super’ El Niño is over, but La Niña looms
The 2015–2016 El Niño has officially ended while its meteorological sister, La Niña, brews.
-
 Climate
ClimateVolcanic rocks help turn carbon emissions to stone — and fast
A pilot program in Iceland that injected carbon dioxide into basaltic lava rocks turned more than 95 percent of the greenhouse gas into stone within two years.
-
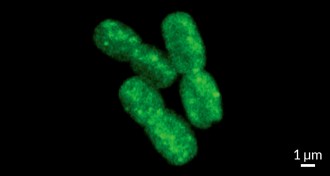 Ecosystems
EcosystemsOcean plankton held hostage by pirate viruses
The most abundant photosynthesizers on Earth stop storing carbon when they catch a virus.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthSpy satellites reveal early start to Antarctic ice shelf collapse
Declassified spy satellite images reveal that Antarctica’s Larsen B ice shelf began destabilizing decades earlier than previously thought.