Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSandboxes keep chicken parasites at bay
Fluffing feathers in sand and dust prevents severe mite infections in cage-free hens.
-
 Earth
EarthWhere the young hot Earth cached its gold
A simulation of the infant Earth provides a new view of how the iron-loving precious metals ended up buried deep in the planet’s core.
-
 Oceans
OceansFish escapes from marine farms raise concerns about wildlife
Farmed salmon, sea bass and other fish frequently escape from sea cages into the ocean. Will these runaways harm native wildlife?
By Roberta Kwok -
 Earth
EarthWave-thumping ‘weather bomb’ storms send elusive S waves through Earth
A rare type of deep-Earth tremor called an S wave generated by a rapidly strengthening storm could help scientists map the planet’s mantle and core.
-
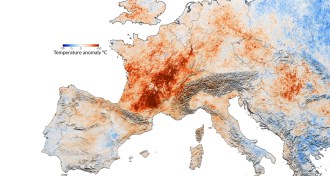 Climate
ClimateGlobal warming amplified death toll during 2003 European heat wave
Climate change caused hundreds of fatalities in London and Paris during the 2003 European heat wave, simulations suggest.
-
 Plants
PlantsHow a tomato plant foils a dreaded vampire vine
Tomatoes can foil a dodder plant attack by getting scared and scabbing over.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsWays to beat heat have hidden costs for birds
Birds that look as if they’re coping with heat waves and climate change may actually be on a downward slide, with underappreciated disadvantages of panting and seeking shade.
By Susan Milius -
 Oceans
OceansLack of nutrients stalled rebound of marine life post-Permian extinction
Warm sea surface temperatures slowed the nitrogen cycle in Earth’s oceans and delayed the recovery of life following the Permian extinction, researchers propose.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEvidence piles up for popular pesticides’ link to pollinator problems
Neonicotinoid pesticides linked to population declines in California butterflies and wild bee extinctions in Great Britain.
-
 Earth
EarthAmericas’ hookup not so ancient after all
Debate lingers over when the Isthmus of Panama formed and closed the seaway that separated North and South America millions of years ago.
-
 Earth
EarthGeneral relativity has readers feeling upside down
Readers respond to the June 25, 2016, issue of Science News with questions on Earth's age, moaning whales, plate tectonics and more.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentNew desalination tech could help quench global thirst
Designed with better, more energy-efficient materials, next-generation desalination plants may offer a way to meet the world’s growing need for freshwater.