Chemistry
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Chemistry
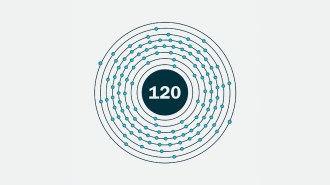
ChemistryA new element on the periodic table might be within reach
Scientists made the known element 116 with a beam of titanium atoms, a technique that could be used to make the undiscovered element 120.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSulfur was key to the first water on Earth
Hydrogen bonded with sulfur may have given our world its first water after the hydrogen broke away and joined with oxygen in the planet’s crust.
By Ken Croswell -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceJurassic Park’s amber-preserved dino DNA is now inspiring a way to store data
DNA is capable of encoding all sorts of data. Storing it in an amberlike material may keep that information safe for nearly forever.
By Payal Dhar -
 Environment
EnvironmentLandfills belch toxic ‘forever chemicals’ into the air
An analysis of samples from three Florida landfills shows that landfill gas can carry more PFAS than the liquid that leaches from the waste.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Chemistry
Chemistry‘Flavorama’ guides readers through the complex landscape of flavor
In her new book, Arielle Johnson, former resident scientist at the restaurant Noma, explains how to think like a scientist in the kitchen.
By Karen Kwon -
 Chemistry
ChemistryA new method of making diamonds doesn’t require extreme pressure
Lab-grown diamonds can form at atmospheric pressure in a liquid of gallium, iron, nickel and silicon.
-
 Space
SpaceHow a sugar acid crucial for life could have formed in interstellar clouds
Computer calculations and lab experiments have revealed a possible mechanism for the creation of glyceric acid, which has been seen in meteorites.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryProtein whisperer Oluwatoyin Asojo fights neglected diseases
Oluwatoyin Asojo’s work on hookworm protein structures have contributed to a vaccine being tested in people.
By Carmen Drahl -
 Humans
HumansThese are the chemicals that give teens pungent body odor
Steroids and high levels of carboxylic acids in teenagers’ body odor give off a mix of pleasant and acrid scents.
By Skyler Ware -
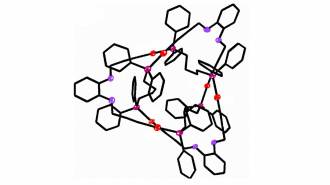 Chemistry
ChemistryThe smallest known molecular knot is made of just 54 atoms
Chemists are still trying to figure out why this combination of gold, phosphorus, oxygen and carbon atoms resulted in a molecular knot in the first place.
By Anna Gibbs -
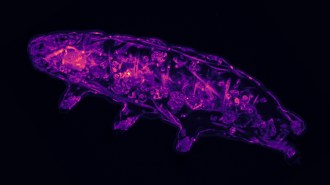 Chemistry
ChemistryHere’s how tardigrades go into suspended animation
A new study offers more clues about the role of oxidation in signaling transitions between alive and mostly dead in tardigrades.
-
 Climate
ClimateCapturing methane from the air would slow global warming. Can it be done?
Removing methane from the atmosphere requires different technology from removing carbon dioxide. Scientists are taking on the challenge.